I haven’t posted anything recently about the European Space Agency’s Euclid mission, but I can remedy that by passing on a new image with text from the accompanying press release. This is actually just one of a batch of new science results emerging from the first `Quick Release’ (Q1) data; I blogged about the first set of Q1 results here.
Incidentally, I find the picture is very reminiscent of a famous painting by James McNeill Whistler.
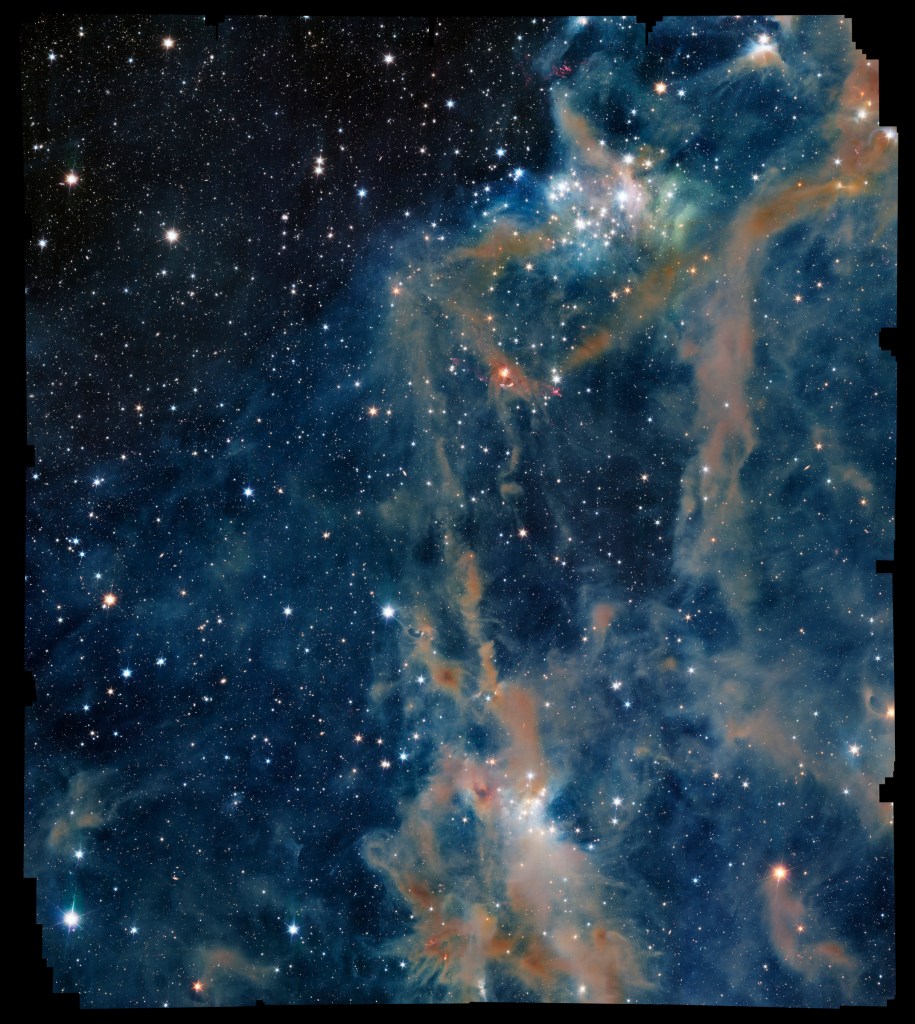
Image description: The focus of the image is a portion of LDN 1641, an interstellar nebula in the constellation of Orion. In this view, a deep-black background is sprinkled with a multitude of dots (stars) of different sizes and shades of bright white. Across the sea of stars, a web of fuzzy tendrils and ribbons in varying shades of orange and brown rises from the bottom of the image towards the top-right like thin coils of smoke.
Technical details: The colour image was created from NISP observations in the Y-, J- and H-bands, rendered blue, green and red, respectively. The size of the image is 11 232 x 12 576 pixels. The jagged boundary is due to the gaps in the array of NISP’s sixteen detectors, and the way the observations were taken with small spatial offsets and rotations to create the whole image. This is a common effect in astronomical wide-field images.
Accompanying Press Release
The above view of interstellar gas and dust was captured by the European Space Agency’s Euclid space telescope. The nebula is part of a so-called dark cloud, named LDN 1641. It sits at about 1300 light-years from Earth, within a sprawling complex of dusty gas clouds where stars are being formed, in the constellation of Orion.
This is because dust grains block visible light from stars behind them very efficiently but are much less effective at dimming near-infrared light.
The nebula is teeming with very young stars. Some of the objects embedded in the dusty surroundings spew out material – a sign of stars being formed. The outflows appear as magenta-coloured spots and coils when zooming into the image.
In the upper left, obstruction by dust diminishes and the view opens toward the more distant Universe with many galaxies lurking beyond the stars of our own galaxy.
Euclid observed this region of the sky in September 2023 to fine-tune its pointing ability. For the guiding tests, the operations team required a field of view where only a few stars would be detectable in visible light; this portion of LDN 1641 proved to be the most suitable area of the sky accessible to Euclid at the time.
The tests were successful and helped ensure that Euclid could point reliably and very precisely in the desired direction. This ability is key to delivering extremely sharp astronomical images of large patches of sky, at a fast pace. The data for this image, which is about 0.64 square degrees in size – or more than three times the area of the full Moon on the sky – were collected in just under five hours of observations.
Euclid is surveying the sky to create the most extensive 3D map of the extragalactic Universe ever made. Its main objective is to enable scientists to pin down the mysterious nature of dark matter and dark energy.
Yet the mission will also deliver a trove of observations of interesting regions in our galaxy, like this one, as well as countless detailed images of other galaxies, offering new avenues of investigation in many different fields of astronomy.
In visible light this region of the sky appears mostly dark, with few stars dotting what seems to be a primarily empty background. But, by imaging the cloud with the infrared eyes of its NISP instrument, Euclid reveals a multitude of stars shining through a tapestry of dust and gas.