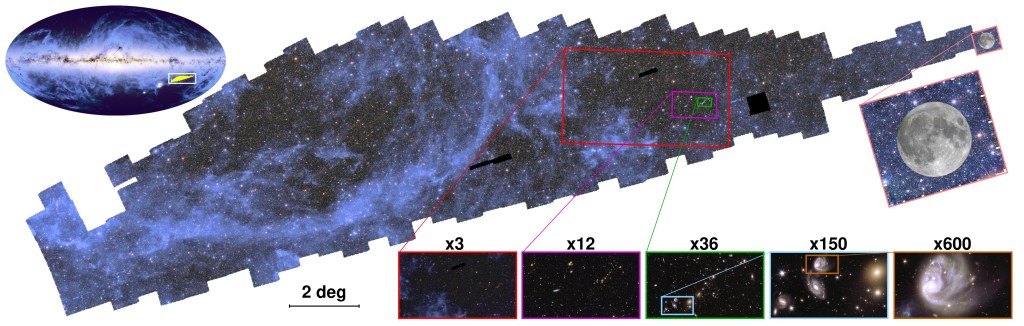
Today is Q1 Day! This means the first public release of data from the full Euclid Survey. It’s only a very small portion (0.4%) of the survey – just 63 square degrees on the sky, while the full survey will be over 14,000 square degrees – but in contrast to earlier data releases, this has been passed through the full Euclid Ground Segment so it represents the true quality of the data we can expect for the rest of the mission. There are no actual cosmology results yet – there isn’t enough data to address the key science goals of Euclid – but there are some great illustrations of the many byproducts of a survey of this type.
Update: here’s one of the Cosmology Talks video by Shaun Hotchkiss with two members of the Euclid Consortium commenting on today’s data release:
As well as the splash of press coverage likely to follow the lifting of today’s embargo, there will be a deluge of Q1-related papers hit the arXiv on 20th March. You can find details here.
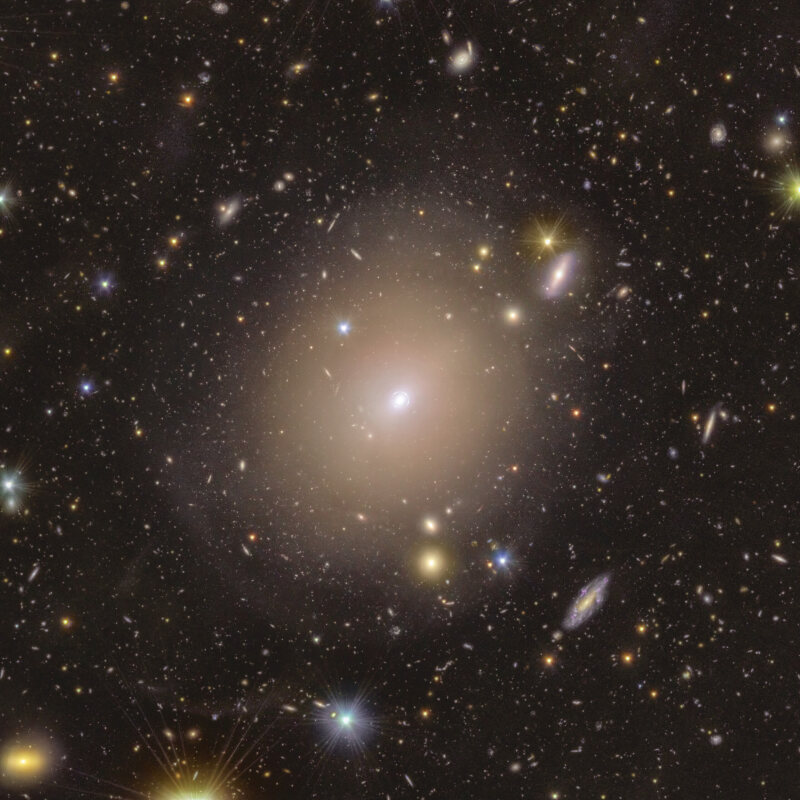
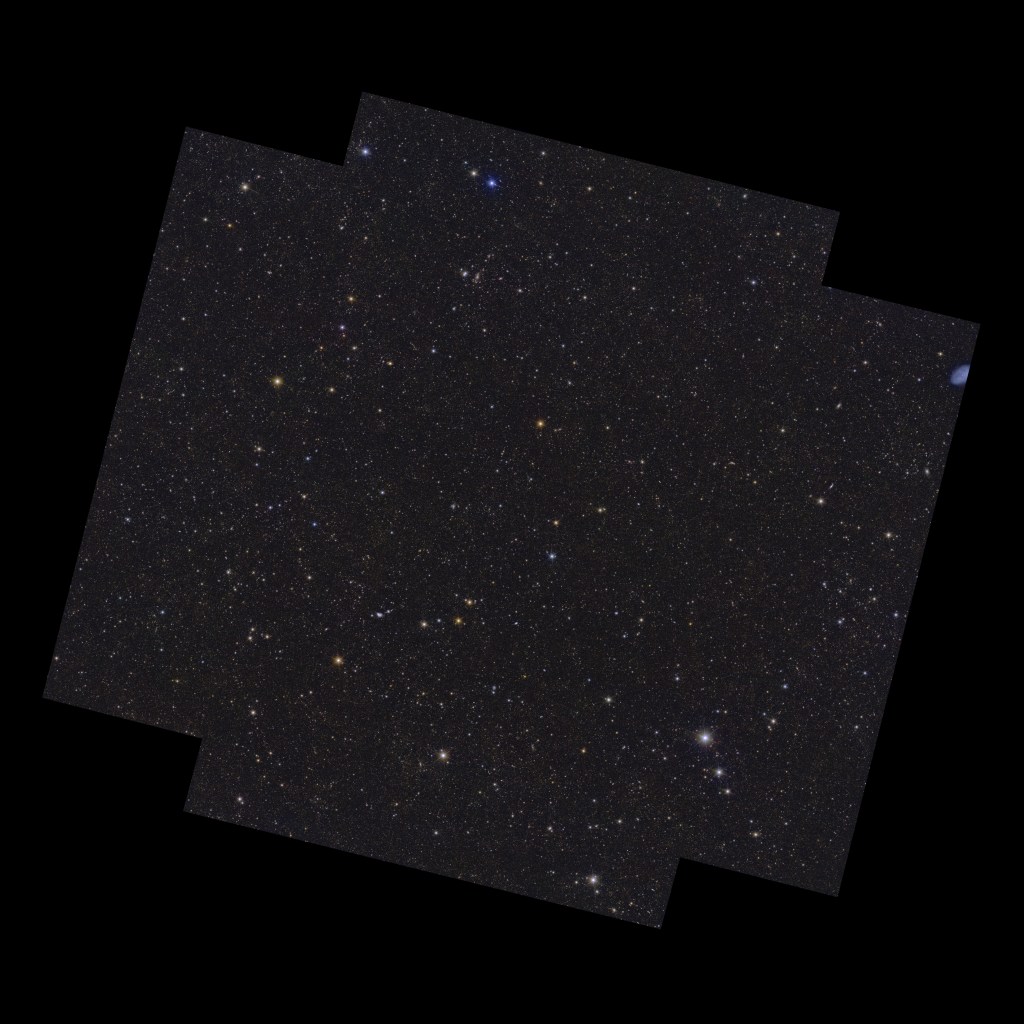
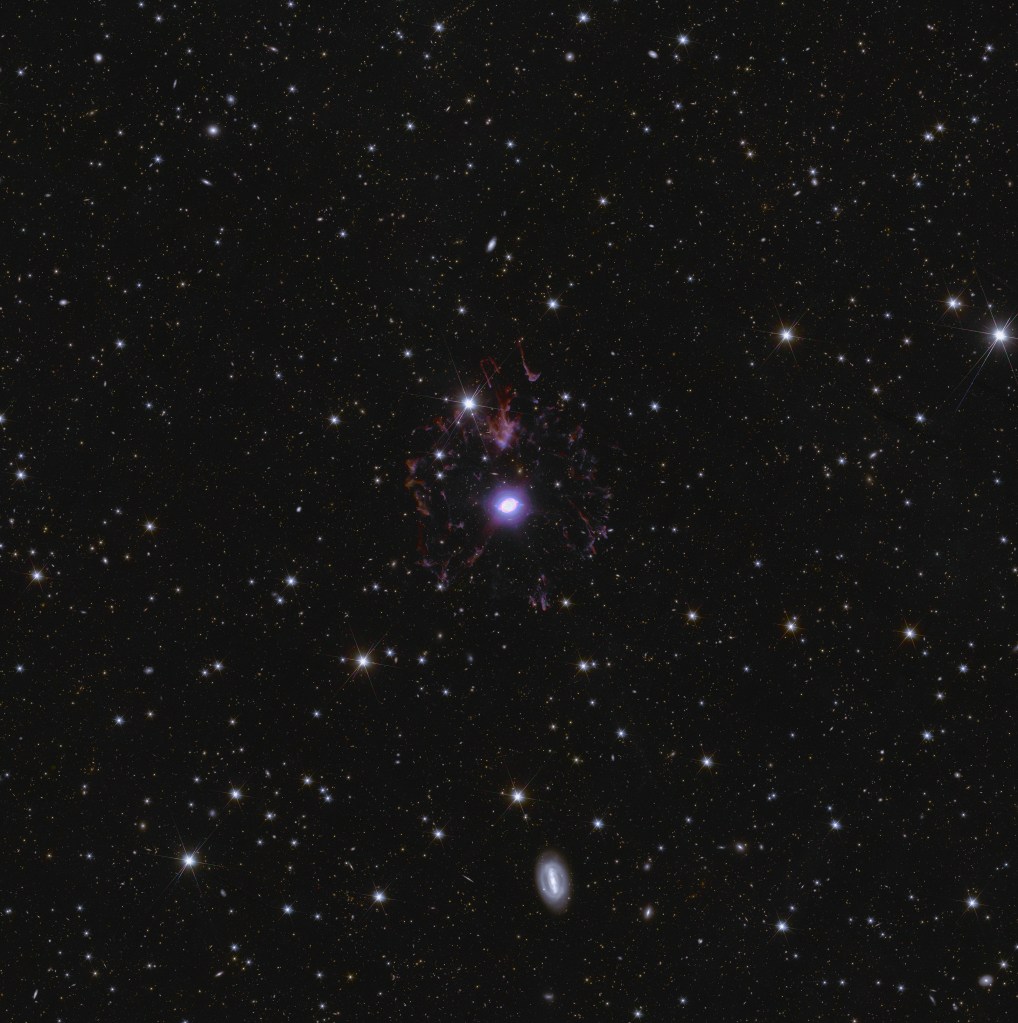
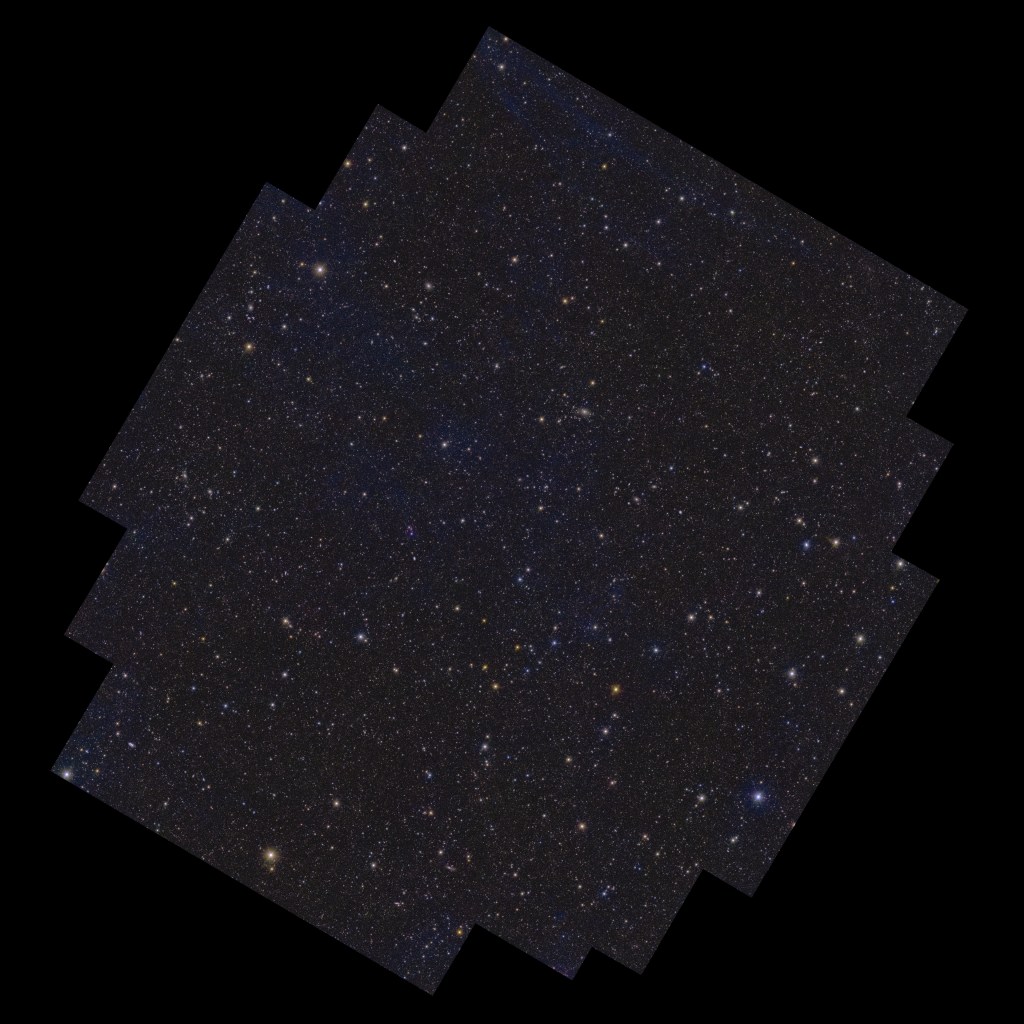
Here’s a gallery of pretty pictures released today. These are low resolution versions; try opening the image in a new tab to see it without the caption. You can find and explore higher resolution images on ESASky (see below). Picture credits are: ESA/Euclid/Euclid Consortium/NASA, image processing by J.-C. Cuillandre, E. Bertin, G. Anselmi for the first six images, then ESA/Euclid/Euclid Consortium/NASA, image processing by M. Walmsley, M. Huertas-Company, J.-C. Cuillandre for the next two (bottom row); and ESA/Euclid/Euclid Consortium/NASA; ESA/Gaia/DPAC; ESA/Planck Collaboration for the last one.
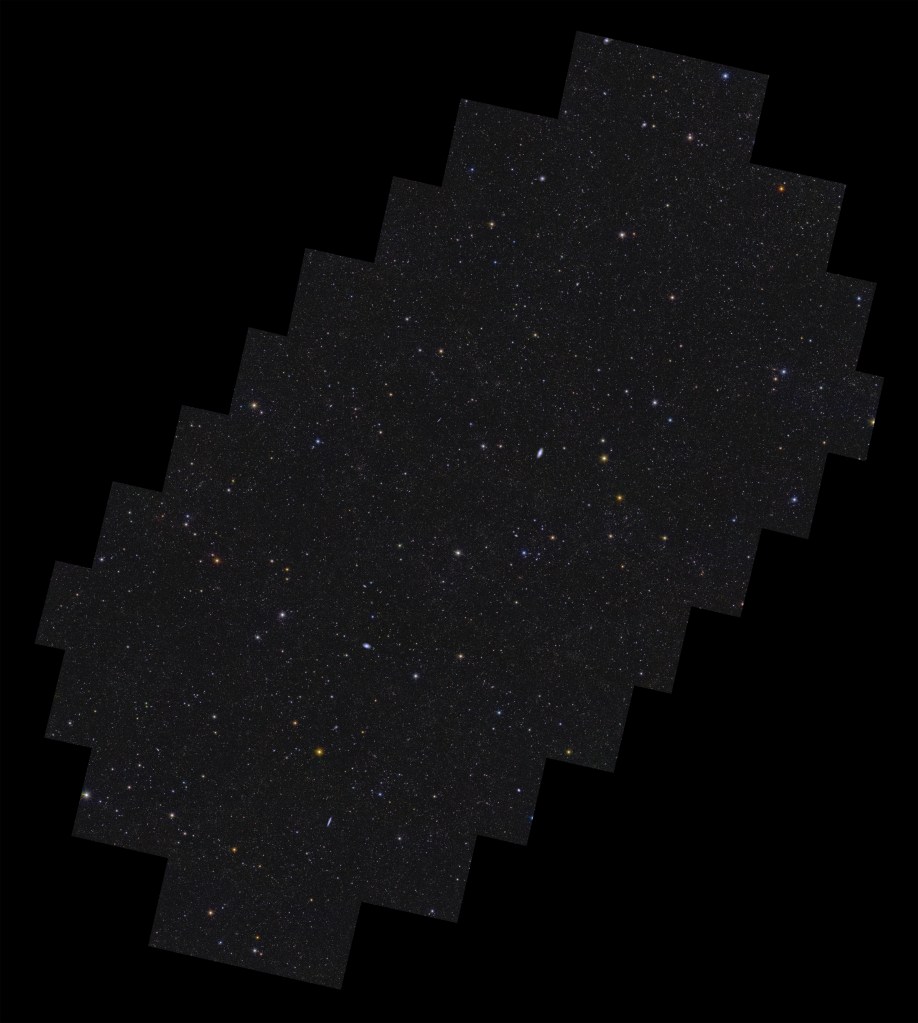








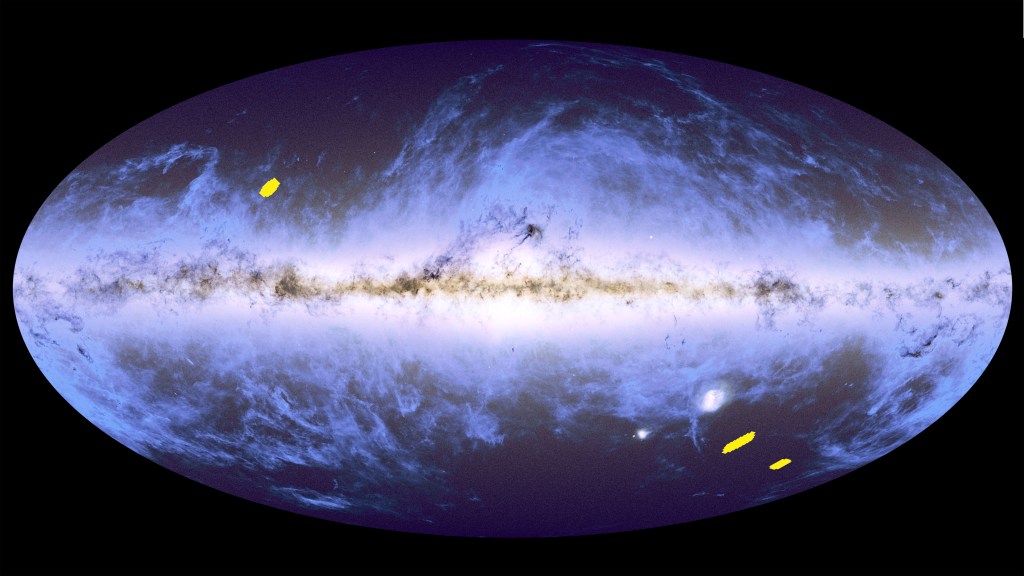
This all-sky view is an overlay of ESA Gaia’s star map from its second data release in 2018 and ESA Planck’s dust map from 2014.
I’m taking the liberty to append the official ESA Press Release, which follows:
–o–
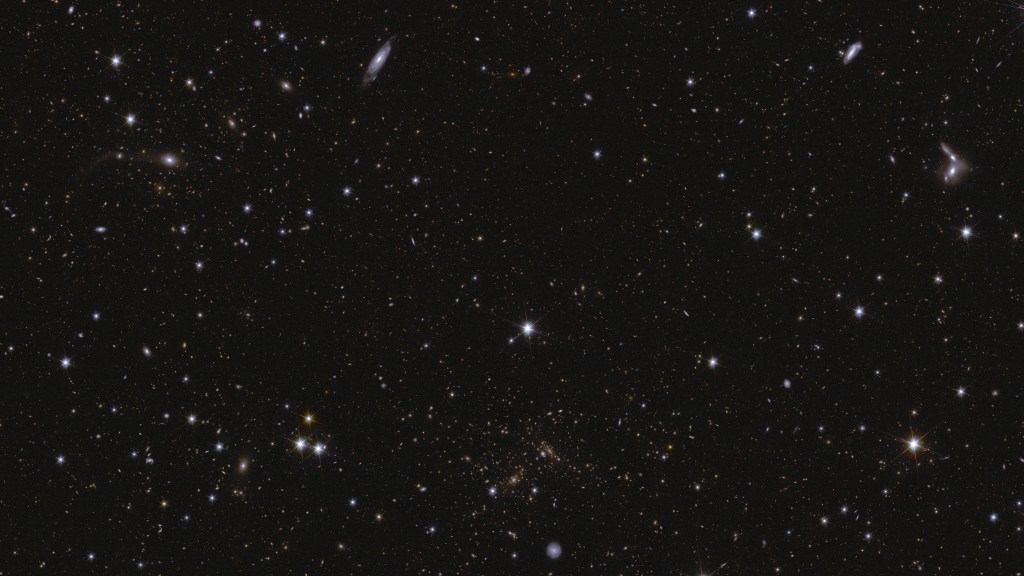
On 19 March 2025, the European Space Agency’s Euclid mission released its first batch of survey data, including a preview of its deep fields. Here, hundreds of thousands of galaxies in different shapes and sizes take centre stage and show a glimpse of their large-scale organisation in the cosmic web.
Covering a huge area of the sky in three mosaics, the data release also includes numerous galaxy clusters, active galactic nuclei and transient phenomena, as well as the first classification survey of more than 380,000 galaxies and 500 gravitational lens candidates compiled through combined artificial intelligence and citizen science efforts. All of this sets the scene for the broad range of topics that the dark Universe detective Euclid is set to address with its rich dataset.
“Euclid shows itself once again to be the ultimate discovery machine. It is surveying galaxies on the grandest scale, enabling us to explore our cosmic history and the invisible forces shaping our Universe,” says ESA’s Director of Science, Prof. Carole Mundell.
“With the release of the first data from Euclid’s survey, we are unlocking a treasure trove of information for scientists to dive into and tackle some of the most intriguing questions in modern science. With this, ESA is delivering on its commitment to enable scientific progress for generations to come.”
Tracing out the cosmic web in Euclid’s deep fields
Euclid has scouted out the three areas in the sky where it will eventually provide the deepest observations of its mission. In just one week of observations, with one scan of each region so far, Euclid already spotted 26 million galaxies. The farthest of those are up to 10.5 billion light-years away. The fields also contain a small population of bright quasars that can be seen much farther away. In the coming years, Euclid will pass over these three regions tens of times, capturing many more faraway galaxies, making these fields truly ‘deep’ by the end of the nominal mission in 2030.
But the first glimpse of 63 square degrees of the sky, the equivalent area of more than 300 times the full Moon, already gives an impressive preview of the scale of Euclid’s grand cosmic atlas when the mission is complete. This atlas will cover one-third of the entire sky – 14 000 square degrees – in this high-quality detail.
“It’s impressive how one observation of the deep field areas has already given us a wealth of data that can be used for a variety of purposes in astronomy: from galaxy shapes, to strong lenses, clusters, and star formation, among others,” says Valeria Pettorino, ESA’s Euclid project scientist. “We will observe each deep field between 30 and 52 times over Euclid’s six year mission, each time improving the resolution of how we see those areas, and the number of objects we manage to observe. Just think of the discoveries that await us.”
To answer the mysteries it is designed for, Euclid measures the huge variety of shapes and the distribution of billions of galaxies very precisely with its high-resolution imaging visible instrument (VIS), while its near-infrared instrument (NISP) is essential for unravelling galaxy distances and masses. The new images already showcase this capability for hundreds of thousands of galaxies, and start to hint at the large-scale organisation of these galaxies in the cosmic web. These filaments of ordinary matter and dark matter weave through the cosmos, and from these, galaxies formed and evolved. This is an essential piece in the puzzle towards understanding the mysterious nature of dark matter and dark energy, which together appear to make up 95% of the Universe.
“The full potential of Euclid to learn more about dark matter and dark energy from the large-scale structure of the cosmic web will be reached only when it has completed its entire survey. Yet the volume of this first data release already offers us a unique first glance at the large-scale organisation of galaxies, which we can use to learn more about galaxy formation over time,” says Clotilde Laigle, Euclid Consortium scientist and data processing expert based at the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris, France.
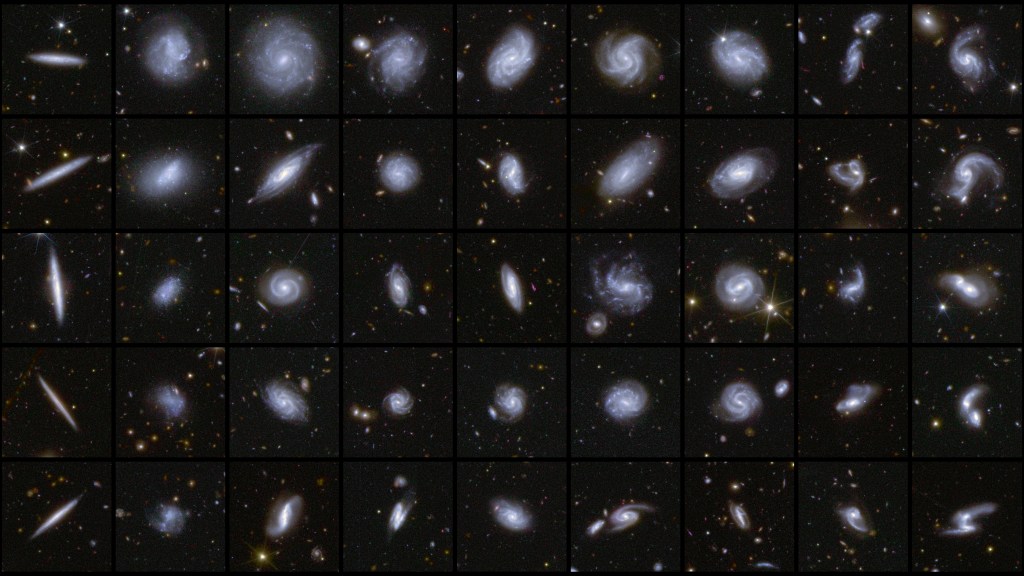
Humans and AI classify more than 380 000 galaxies
Euclid is expected to capture images of more than 1.5 billion galaxies over six years, sending back around 100 GB of data every day. Such an impressively large dataset creates incredible discovery opportunities, but huge challenges when it comes to searching for, analysing and cataloguing galaxies. The advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, in combination with thousands of human citizen science volunteers and experts, is playing a critical role.
“We’re at a pivotal moment in terms of how we tackle large-scale surveys in astronomy. AI is a fundamental and necessary part of our process in order to fully exploit Euclid’s vast dataset,” says Mike Walmsley, Euclid Consortium scientist based at the University of Toronto, Canada, who has been heavily involved in astronomical deep learning algorithms for the last decade.
“We’re building the tools as well as providing the measurements. In this way we can deliver cutting-edge science in a matter of weeks, compared with the years-long process of analysing big surveys like these in the past,” he adds.
A major milestone in this effort is the first detailed catalogue of more than 380 000 galaxies, which have been classified according to features such as spiral arms, central bars, and tidal tails that infer merging galaxies. The catalogue is created by the ‘Zoobot’ AI algorithm. During an intensive one-month campaign on Galaxy Zoo last year, 9976 human volunteers worked together to teach Zoobot to recognise galaxy features by classifying Euclid images.
This first catalogue released today represents just 0.4% of the total number of galaxies of similar resolution expected to be imaged over Euclid’s lifetime. The final catalogue will present the detailed morphology of at least an order of magnitude more galaxies than ever measured before, helping scientists answer questions like how spiral arms form and how supermassive black holes grow.
“We’re looking at galaxies from inside to out, from how their internal structures govern their evolution to how the external environment shapes their transformation over time,” adds Clotilde.
“Euclid is a goldmine of data and its impact will be far-reaching, from galaxy evolution to the bigger-picture cosmology goals of the mission.”
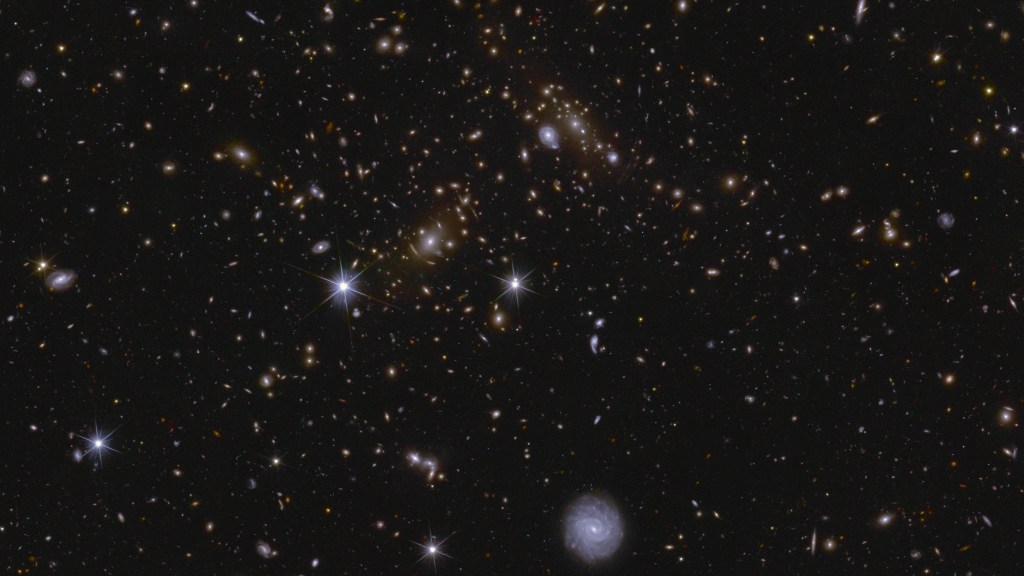
Gravitational lensing discovery engine
Light travelling towards us from distant galaxies is bent and distorted by normal and dark matter in the foreground. This effect is called gravitational lensing and it is one of the tools that Euclid uses to reveal how dark matter is distributed through the Universe.
When the distortions are very apparent, it is known as ‘strong lensing’, which can result in features such as Einstein rings, arcs, and multiple imaged lenses.
Using an initial sweep by AI models, followed by citizen science inspection, expert vetting and modelling, a first catalogue of 500 galaxy-galaxy strong lens candidates is released today, almost all of which were previously unknown. This type of lensing happens when a foreground galaxy and its halo of dark matter act as a lens, distorting the image of a background galaxy along the line of sight towards Euclid.
With the help of these models, Euclid will capture some 7000 candidates in the major cosmology data release planned for the end of 2026, and in the order of 100 000 galaxy-galaxy strong lenses by the end of the mission, around 100 times more than currently known.
Euclid will also be able to measure ‘weak’ lensing, when the distortions of background sources are much smaller. Such subtle distortions can only be detected by analysing large numbers of galaxies in a statistical way. In the coming years, Euclid will measure the distorted shapes of billions of galaxies over 10 billion years of cosmic history, thus providing a 3D view of the distribution of dark matter in our Universe.
“Euclid is very quickly covering larger and larger areas of the sky thanks to its unprecedented surveying capabilities,” says Pierre Ferruit, ESA’s Euclid mission manager, who is based at ESA’s European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) in Spain, home of the Astronomy Science Archive where Euclid’s data will be made available.
“This data release highlights the incredible potential we have by combining the strengths of Euclid, AI, citizen science and experts into a single discovery engine that will be essential in tackling the vast volume of data returned by Euclid.”
Notes to editors
As of 19 March 2025, Euclid has observed about 2000 square degrees, approximately 14% of the total survey area (14 000 square degrees). The three deep fields together comprise 63.1 square degrees.
Euclid ‘quick’ releases, such as the one of 19 March, are of selected areas, intended to demonstrate the data products to be expected in the major data releases that follow, and to allow scientists to sharpen their data analysis tools in preparation. The mission’s first cosmology data will be released to the community in October 2026. Data accumulated over additional, multiple passes of the deep field locations will be included in the 2026 release.
The three deep field previews can now be explored in ESASky from 19 March 12:00 CET onwards:
- Euclid Deep Field South: https://sky.esa.int/esasky/?hide_welcome=true&hide_banner_info=true&hips=DES-DR2+ColorIRG&sci=false&layout=esasky&euclid_image=EDFS
- Euclid Deep Field Fornax: https://sky.esa.int/esasky/?hide_welcome=true&hide_banner_info=true&hips=PanSTARRS+DR1+color+(i%2C+r%2C+g)&sci=false&layout=esasky&euclid_image=EDFF
- Euclid Deep Field North: https://sky.esa.int/esasky/?hide_welcome=true&hide_banner_info=true&hips=PanSTARRS+DR1+color+(i%2C+r%2C+g)&sci=false&layout=esasky&euclid_image=EDFN
The data release of 19 March 2025 is described in multiple scientific papers which have not yet been through the peer-review process, but which will be submitted to the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. A preprint of the papers is available here from 19 March 12:00 CET.
Find more detailed information about the data release here.
About Euclid
Euclid was launched in July 2023 and started its routine science observations on 14 February 2024. In November 2023 and May 2024, the world got its first glimpses of the quality of Euclid’s images, and in October 2024 the first piece of its great map of the Universe was released.
Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by ESA, with contributions from its Member States and NASA. The Euclid Consortium – consisting of more than 2000 scientists from 300 institutes in 15 European countries, the USA, Canada and Japan – is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis. ESA selected Thales Alenia Space as prime contractor for the construction of the satellite and its service module, with Airbus Defence and Space chosen to develop the payload module, including the telescope. NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP. Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.
Contact: ESA Media relations (media@esa.int)