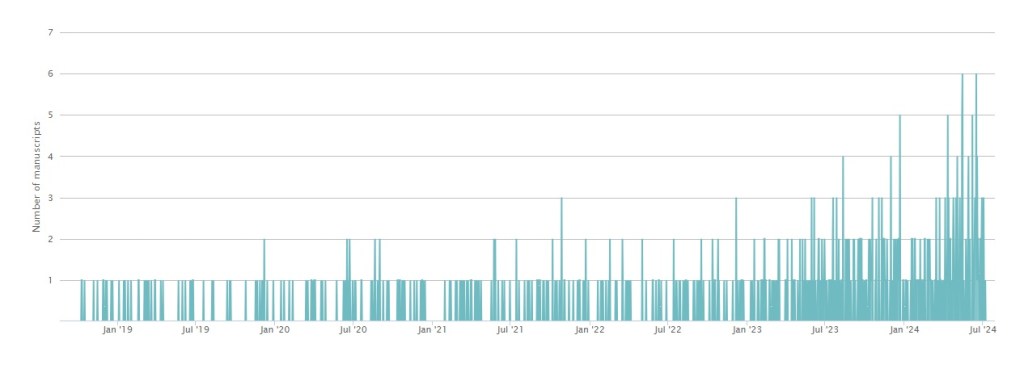
It’s Saturday morning so it’s time for the usual weekly update of publications at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Once again this week’s report will be short because there is only one paper to report this week, being the 69th paper in Volume 7 (2024) and the 184th altogether. It was published on Wednesday 21st August 2024.
This week has been a bit strange, actually. We have actually accepted four papers that I was expecting to publish this week but only one has been published because the authors of the others have not yet put the final versions on arXiv. I suppose this is due to ongoing holidays and they’ll appear in due course. The other thing that happened was that when I published the paper below I discovered that the Crossref system was down for a scheduled upgrade that took a whole day to complete. Although I published the paper on 21st August I couldn’t register the metadata, etc, until 22nd August. Just as well I didn’t have more to do really!
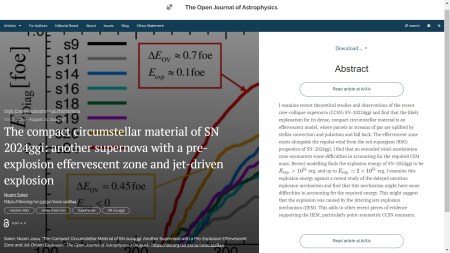
Anyway, the title of the latest paper is is The compact circumstellar material of SN 2024ggi: another supernova with a pre-explosion effervescent zone and jet-driven explosion and it is in the folder marked High-Energy Astrophysical Phenomena. The author is Noam Soker of Technion, Haifa, in Israel; the paper presents a possible explanation of then properties of recently-observed supernova SN 2024ggi.
Here is the overlay of the paper containing the abstract:
You can click on the image of the overlay to make it larger should you wish to do so. You can also find the officially accepted version of the paper on the arXiv here.