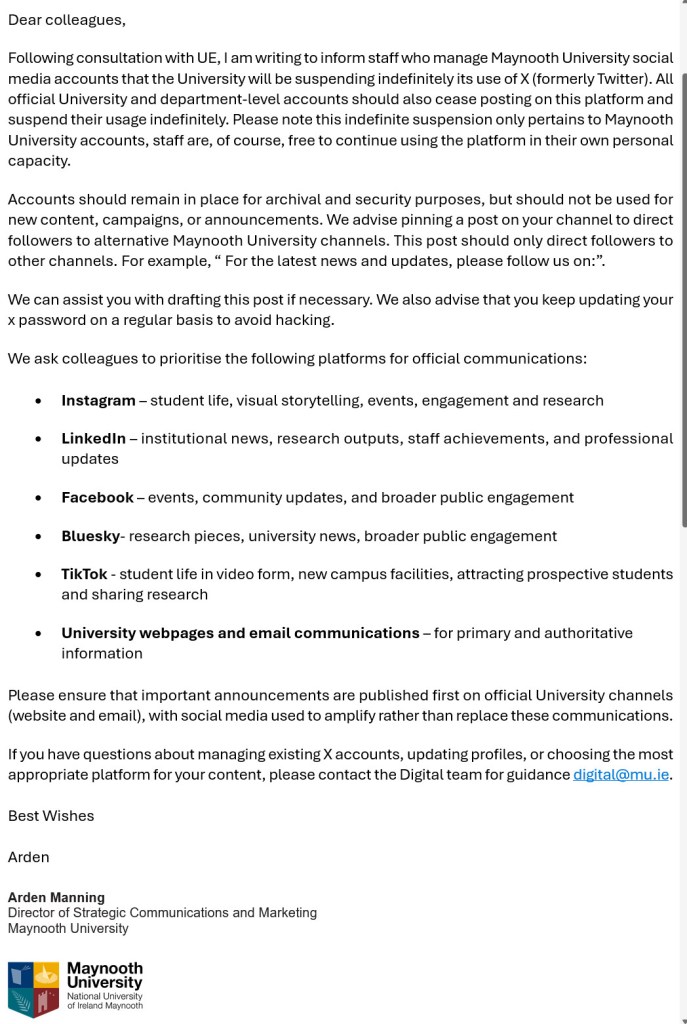
I’ve posted a number of items recently (e.g. here) about why public institutions in Ireland (and anywhere else, for that matter) should not be using X. I noticed today a message on BlueSky containing the following clear and compelling letter from a number of commuter organizations to Irish Rail (Iarnród Éireann), which can be found here but which I’m taking the liberty of sharing in full here to amplify.
–o–
We are writing as rail and commuter advocacy groups across Ireland, to request that Iarnród Éireann move its real-time service updates regarding cancellations and delays from the social media platform X (formerly Twitter) to your own website and official channels.
Currently, passengers seeking up-to-date information about service disruptions must have an active X account to view these critical updates. This creates several significant problems:
Accessibility Concerns: Requiring passengers to maintain an account on a third-party social media platform to access essential public transport information creates an unnecessary barrier. Many passengers, particularly elderly travellers or those who choose not to use social media, are effectively excluded from receiving timely service updates.
Platform Concerns: Recent controversies surrounding X, including serious issues with child safety and content moderation failures involving Grok AI, make it an increasingly inappropriate platform for a state-owned public service to rely upon as its primary and in some cases, only communication channel. Iarnród Éireann should not require its customers to engage with a platform facing such significant ethical and safety concerns. Dublin City Council have this week stopped posting on the platform because of these concerns.
Service Reliability: Relying on a third-party platform also creates vulnerability. Changes to X’s policies, accessibility, or availability are beyond Iarnród Éireann’s control and could impact passengers’ access to vital travel information. EU and Irish law limiting access to these platforms for under 16’s could be introduced in the coming years which would remove the ability for young people to receive up to date journey information.
I would respectfully suggest that Iarnród Éireann implement real-time service updates (including information on delays/cancellations/amendments) directly on irishrail.ie , along with TFI Live and the Irish Rail app, where they can be freely accessed by all passengers without requiring any third-party account. This information is essential public service data and should be universally accessible.
Recommendations for Improved Service Communication
Beyond relocating updates to your own platform, we would like to suggest several improvements to how disruption information is communicated to passengers:
Clear Alternative Transport Information: When disruptions occur, guidance on alternative transport options is often vague or incomplete. For example, announcements stating “Dublin Bus will accept tickets” leave passengers uncertain whether LUAS, Go-Ahead, or LocalLink services are also available. Clear, specific information about all accepted alternative services would significantly reduce passenger confusion and stress during disruptions. Additionally, when a delay does occur, stating ‘operational issues’ does not allow commuters to determine the length of disruption. Commuters could utilise alternate modes of transport in the event of disruption, but cannot make the decision on whether to do so or not without clear information from Iarnrod Éireann. Other international providers have recently switched to a more detailed information provision in the events of issues or delays. For example, Dutch Railways, instead of saying ‘operational reasons’ now say ‘a fallen wire, or broken down train’ that allow passengers to more accurately determine whether to find alternative transport or to wait. It may also be useful to include a scale, letting the customer know whether or not the incident is minor, notable, or major where possible.
Visual Aids and Information Hierarchy: Reading lengthy blocks of text to understand service disruptions is inadequate, particularly for passengers trying to quickly assess their options whilst at stations or en route. Disruption information would benefit greatly from visual aids such as maps showing affected sections, clear headings, and structured information that allows passengers to quickly grasp the extent and nature of disruptions. A balance must be struck between providing sufficient detail and maintaining clarity.
Integration with Journey Planning Tools: Iarnród Éireann maintains a GTFS (General Transit Feed Specification) data feed that enables real-time information to be pushed to the TFI Live app and third-party applications such as Google Maps or Transit. We strongly encourage Iarnród Éireann to utilise this capability fully, ensuring that disruption information reaches passengers through the multiple platforms they already use for journey planning.
Location-Specific Disruption Guides: For locations where service disruptions occur regularly, Iarnród Éireann should provide dedicated journey planning resources. For instance, a guide explaining “My train has broken down in Greystones, what services can I access from here and where can I find further disruption information?” would be invaluable. Such resources would empower passengers to make informed decisions quickly during stressful situations.
We would appreciate your consideration of this matter and look forward to your response.
South East on Track, Cork Commuter Coalition, Dublin Commuter Coalition, Galway Commuter Coalition.