It’s Saturday morning once again so here’s another quick update of activity at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Since the last update a week ago we have published four papers, which takes the count in Volume 7 (2024) up to 114 and the total published altogether by OJAp up to 229. If we publish just one more paper between now and the end of the year, we will have published as many papers in 2024 as we have in all previous years.
Anyway, in chronological order of publication, the four papers published this week, with their overlays, are as follows. You can click on the images of the overlays to make them larger should you wish to do so.
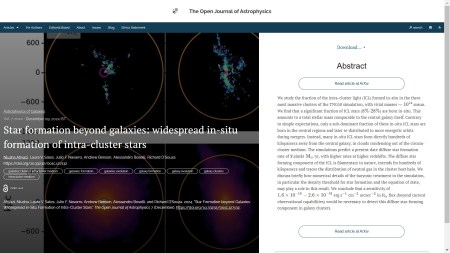
First one up is “Star formation beyond galaxies: widespread in-situ formation of intra-cluster stars” by Niusha Ahvazi & Laura V. Sales (UC Riverside, USA), Julio F. Navarro (U. Victoria, Canada), Andrew Benson (Carnegie Obs. USA), Alessandro Boselli (Aix Marseille U., France) and Richard D’Souza (Vatican Obs.). The paper, which is in the folder marked Astrophysics of Galaxies, The paper presents a simulation-based analysis of a diffuse star forming component in galaxy clusters extending for hundreds of kiloparsecs and tracing the distribution of neutral gas in the cluster host halo.
Here is a screen grab of the overlay, which includes the abstract:
You can find the officially accepted version of the paper on the arXiv here.
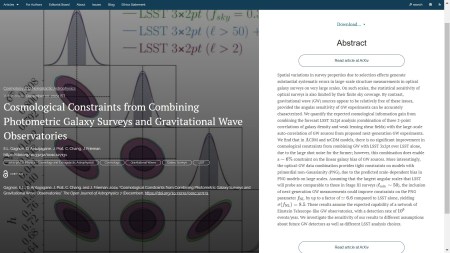
The second paper to announce, published on 10th December 2024 in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics, is “Cosmological Constraints from Combining Photometric Galaxy Surveys and Gravitational Wave Observatories” by E.L. Gagnon, D. Anbajagane, J. Prat, C. Chang, and J. Frieman (all of U. Chicago, USA). This article quantifies the expected cosmological information gain from combining the forecast LSST 3x2pt analysis with the large-scale auto-correlation of GW sources from proposed next-generation GW experiments.
You can see the overlay here:
The accepted version of this paper can be found on the arXiv here.
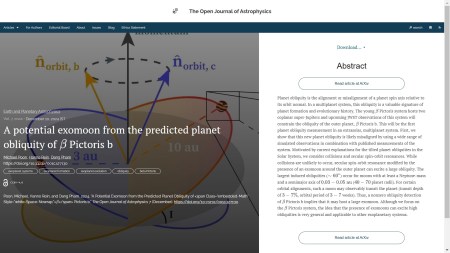
The third paper, also published on 10th December 2024, but in the folder marked Earth and Planetary Astrophysics, has the title “A potential exomoon from the predicted planet obliquity of β Pictoris b” and is written by Michael Poon, Hanno Rein, and Dang Pham all of the University of Toronto, Canada. It presents discussion, based on the β Pictoris system, of the idea that the presence of exomoons can excite misalignment between the spin and orbit axis (obliquity) in exoplanet systems
Here is the overlay
The final version accepted on arXiv is here.
Last of this quartet, published on 11th December 2024, and in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics is “Map-level baryonification: Efficient modelling of higher-order correlations in the weak lensing and thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich fields” and is by Dhayaa Anbajagane & Shivam Pandey (U. Chicago) and Chihway Chang (Columbia U.), all based in the USA.
The paper proposes an extension of the semi-analytic formalism to weak lensing and thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich (tSZ) fields directly on the full-sky, with an emphasis on higher-order correlations. The overlay is here:
You can find the official accepted version on the arXiv here.
That’s all for this week. I’ll do another update next Saturday, and that will probably be the last one of the year. If we publish just one more paper between now and 31st December, we will have published as many papers in 2024 as we have in all previous years put together!