In case you weren’t aware, SciPost is a publishing infrastructure that provides Diamond Open Access to scientific papers. That means they are free to publish and free to read. They are funded by a consortium but are now struggling financially. They have recently circulated an open letter to the Community explaining their predicament and asking for help. I encourage you to read it and, if you can, to make a donation (or bully your institution to do so).
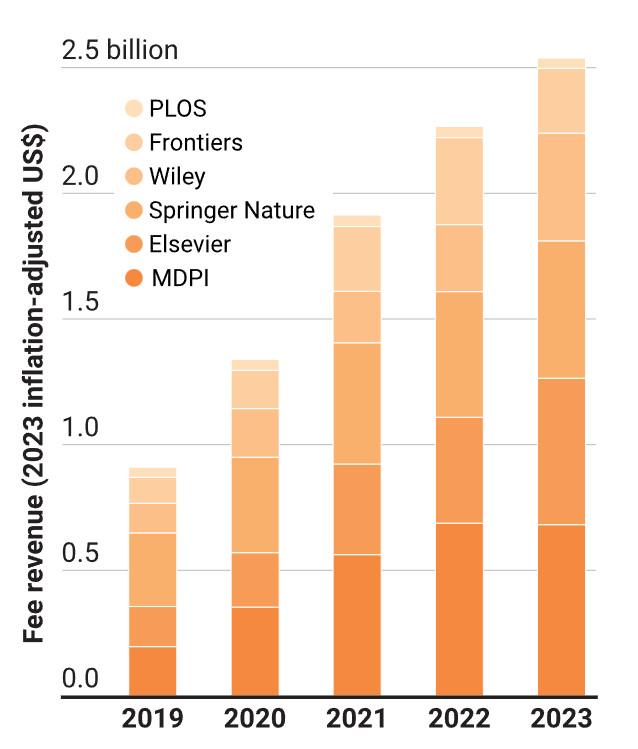
The open letter explains that SciPost is currently running at an average cost per paper of €500. That is much less than a typical APC for a mainstream journal but it is not a negligible cost. At the rate at which SciPost is publishing it amounts to about €1000 per day. SciPost currently attracts a significant level of sponsorship but it is not enough to support its current level of activity. Information on how to help SciPost can be found here. It is a worthy cause and deserves to be supported.
One area in which SciPost has not really taken of is Astronomy, where it has published very few papers. This may at be at least partly because of the Open Journal of Astrophysics (OJAp) which is also Diamond Open Access but runs in a very different and much cheaper way. A full breakdown of costs at OJAp is given here our annual running costs are about €5000 per year, which works out at less than €50 per paper (on average); that comprises a fixed component and a marginal cost of €10 per paper.
The main reasons for the large difference in running costs are: (i) SciPost maintains and runs its own platform; and (ii) it offers a copy-editing service. OJAp piggy-backs on arXiv (where most astrophysics research papers are found anyway) and expects authors to provide the final version of their own work. Neither organization pays referees or Editors. To enable it to run, SciPost employs about three staff full-time (2.9 FTE to be precise); OJAp has no employees and we keep our costs down by offering a ‘no-frills’ service. Instead of having a wide range of sponsors, we are entirely funded by Maynooth University. I am very grateful for that support, but we are run on a shoestring budget.
I have written before about what I think the future of Diamond Open Access could be like. I would like to see a range of Diamond Open Access journals offering a choice for authors and serving different sub-disciplines. Most universities nowadays have publishing operations so there could be network of federated journals, some based on arXiv and some based on other repositories and others with different models, such as SciPost. Perhaps institutions are worried about the expense but, as we have shown the actual cost, is far less than they are wasting on Article Processing Charges.
I don’t see other Diamond Open Access journals as competitors, but as allies with community-led ecosystem. I’d be more than happy to discuss how to start up such a journal on the OJAp model with anyone interested, and have already done so with some interested parties. As far as I’m concerned, the more the merrier! It is neither fair nor reasonable, however, that the expense of running a journal that serves the global astrophysics community should fall entirely on one small University in Ireland.
By all means support SciPost (and get your institutions to do likewise), but please also consider supporting OJAp. We are currently covering our costs but have no funds to make enhancements (such as a much-needed new LaTex template). If you can afford to make a donation to SciPost, then perhaps you can afford to make a donation to OJAp proportionate to our lower running costs? For example, if you give €10K to SciPost, could you give us €1K too? That amount would keep SciPost running for a day and OJAp for many months…