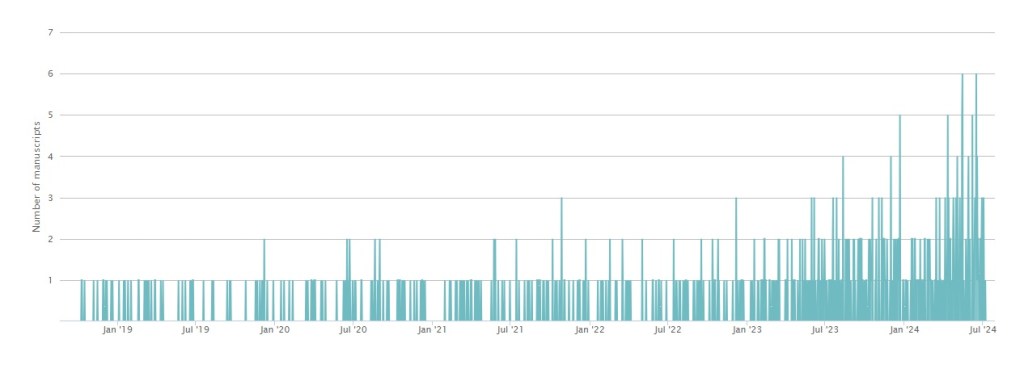
The number of papers submitted to the Open Journal of Astrophysics continues to rise, as demonstrated by this nice graphic which shows the stats for new submissions for the last five years:
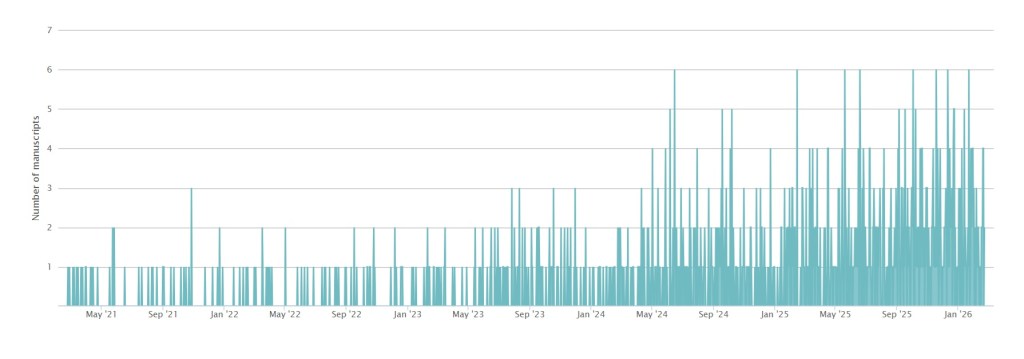
It’s very clear that the thicket is getting thicker! The increasing number of articles is of course very welcome indeed, but it is increasing the load on our Editorial Board and that includes me! I think it’s time therefore to look for more volunteers to join the team, in any area of astrophysics. As a reminder, here are the areas we cover, corresponding to the sections of astro-ph on the arXiv:
- astro-ph.GA – Astrophysics of Galaxies. Phenomena pertaining to galaxies or the Milky Way. Star clusters, HII regions and planetary nebulae, the interstellar medium, atomic and molecular clouds, dust. Stellar populations. Galactic structure, formation, dynamics. Galactic nuclei, bulges, disks, halo. Active Galactic Nuclei, supermassive black holes, quasars. Gravitational lens systems. The Milky Way and its contents
- astro-ph.CO – Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics. Phenomenology of early universe, cosmic microwave background, cosmological parameters, primordial element abundances, extragalactic distance scale, large-scale structure of the universe. Groups, superclusters, voids, intergalactic medium. Particle astrophysics: dark energy, dark matter, baryogenesis, leptogenesis, inflationary models, reheating, monopoles, WIMPs, cosmic strings, primordial black holes, cosmological gravitational radiation
- astro-ph.EP – Earth and Planetary Astrophysics. Interplanetary medium, planetary physics, planetary astrobiology, extrasolar planets, comets, asteroids, meteorites. Structure and formation of the solar system
- astro-ph.HE – High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena. Cosmic ray production, acceleration, propagation, detection. Gamma ray astronomy and bursts, X-rays, charged particles, supernovae and other explosive phenomena, stellar remnants and accretion systems, jets, microquasars, neutron stars, pulsars, black holes
- astro-ph.IM – Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics. Detector and telescope design, experiment proposals. Laboratory Astrophysics. Methods for data analysis, statistical methods. Software, database design
- astro-ph.SR – Solar and Stellar Astrophysics. White dwarfs, brown dwarfs, cataclysmic variables. Star formation and protostellar systems, stellar astrobiology, binary and multiple systems of stars, stellar evolution and structure, coronas. Central stars of planetary nebulae. Helioseismology, solar neutrinos, production and detection of gravitational radiation from stellar systems.
We are looking for experienced scientists in any of these areas, and it would be useful to have people who can cover a range of subjects (as some of our existing editors do). As I mentioned here, our most popular area is 1 (Astrophysics of Galaxies) but 2 (Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics) is running it a close second so I’d particular welcome offers from people with expertise in either of those fields, though Editors in any of the areas listed above would be welcome additions.
Since we don’t charge authors or readers we can not offer payment to Editors but it is nevertheless a way of providing a service to the community.
Please get in touch either through the Open Journal website here, or through a message Mastodon here, or BlueSky here. You could even send a message through this form: