It’s Saturday morning again and time to post an update of activity at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. As last week there are six papers to announce, bringing the count in Volume 7 (2024) up to 93 and the total altogether up to 208.
In chronological order, the six papers published this week, with their overlays, are as follows. You can click on the images of the overlays to make them larger should you wish to do so.
First one up, published on Monday 14th October 2024, is in the folder marked Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics and is called “Backreaction in Numerical Relativity: Averaging on Newtonian gauge-like hypersurfaces in Einstein Toolkit cosmological simulations“. This paper presents a numerical study of the effect of local inhomogeneities on the dynamical evolution of the Universe, i.e. the so-called “backreaction” problem; the authors are Alexander Oestreicher and Sofie Marie Koksbang of the University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark.
Here is a screen grab of the overlay, which includes the abstract:
You can find the officially accepted version of the paper on the arXiv here.
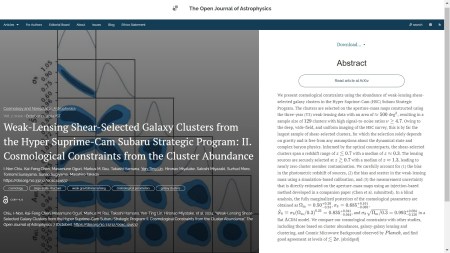
The second paper to announce, published on 15th October 2024, is “Weak-Lensing Shear-Selected Galaxy Clusters from the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program: II. Cosmological Constraints from the Cluster Abundance” by I-Non Chiu (National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan) and 11 others based in Taiwan, Japan, India and the USA. This paper, which is also in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics presents constraints on cosmological parameters obtained from a sample of galaxy clusters
You can see the overlay here:
The accepted version of this paper can be found on the arXiv here.
The third paper is “Image formation near hyperbolic umbilic in strong gravitational lensing” by Ashish Kumar Meena (Ben Gurion University, Israel) and Jasjeet Singh Bagla (IISER Mohali, India). It presents a detailed theoretical discussion of a particular form of strong gravitational lensing and its observational consequences; it is in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies and was published on October 15th 2024.
The overlay is here:
The officially accepted version can be found on arXiv here.
The fourth paper, published on 16th October 2024 and in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, is “Weak Gravitational Lensing around Low Surface Brightness Galaxies in the DES Year 3 Data” by N. Chicoine (University of Chicago, USA) et al. (105 authors; DES Collaboration). It presents a demonstration of the viability of using weak gravitational lensing to constrain the halo masses of low surface brightness galaxies.
The overlay is here
You can find the officially accepted version of this paper here.
The fifth paper in this batch is “Imprints of interaction processes in the globular cluster system of NGC 3640” by Ana I Ennis (Waterloo, Canada) and Juan Pablo Caso & Lilia Patricia Bassino (Instituto de Astrofísica de La Plata, Argentina). This one was also published on 16th October 2024 and is in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, Here is the overlay
You can find the official accepted version on the arXiv here.
Finally for this week we have “On the nature of the C IV-bearing circumgalactic medium at 𝒛∼𝟏” by Suyash Kumar, Hsiao-Wen Chen, Zhijie Qu & Mandy C. Chen (U. Chicago), Fakhri S. Zahedy (U. North Texas), Sean D. Johnson (Carnegie Observatories), Sowgat Muzahid (IUCAA, India) and Sebastiano Cantalupo (U. Milan Bicocca)
The overlay is here
You can find the officially-accepted version on arXiv here.
That’s it for now. More next week!