It’s Saturday morning again, so it’s time again for an update of papers published at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Since the last update we have published seven new papers, which brings the number in Volume 8 (2025) up to 92, and the total so far published by OJAp up to 327.
This was a slightly strange week, starting with the fact that there were no new arXiv announcements on Monday 7th July because of the 4th July holiday in the USA on Friday so no papers were published that day. We were not able to publish any papers on Wednesday 9th July either because Crossref was offline for 24 hours that day while its data was migrated into the cloud. Our publishing process requires a live connection with Crossref to deposit metadata upon publication so we can’t publish while that service is down. Fortunately the update seems to have gone well and normal services resumed the following day. That partially accounts for the fact that four of this week’s papers were published on 10th July.
Anyway, The papers published this week, with their overlays, are as follows. You can click on the images of the overlays to make them larger should you wish to do so.
The first paper to report is “The Jackknife method as a new approach to validate strong lens mass models” by Shun Nishida & Masamune Oguri (Chiba University, Japan) , Yoshinobu Fudamoto (Steward Observatory, USA) and Ayari Kitamura (Tohoku University, Japan). This article, which is in the folder marked Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics, describes and application of the Jackknife statistical resampling techique to gravitational lensing by removing lensed images and recalcualting the mass modelIt was published on Tuesday 8th July 2025. The overlay is here:

The officially-accepted version can be found on arXiv here.
The second paper is “Low redshift post-starburst galaxies host abundant HI reservoirs” by Sara Ellison (U. Victoria, Canada) and 10 others based in China, UK, Spain, USA and Canada. This one was also published oon Tuesday 8th July but in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies. This paper uses 21cm observations of a sample of post-starburst galaxies, to show that they contain large reservoirs of neutral hydrogen. Here is the overlay:

You can find the final version of the manuscript on arXiv here.
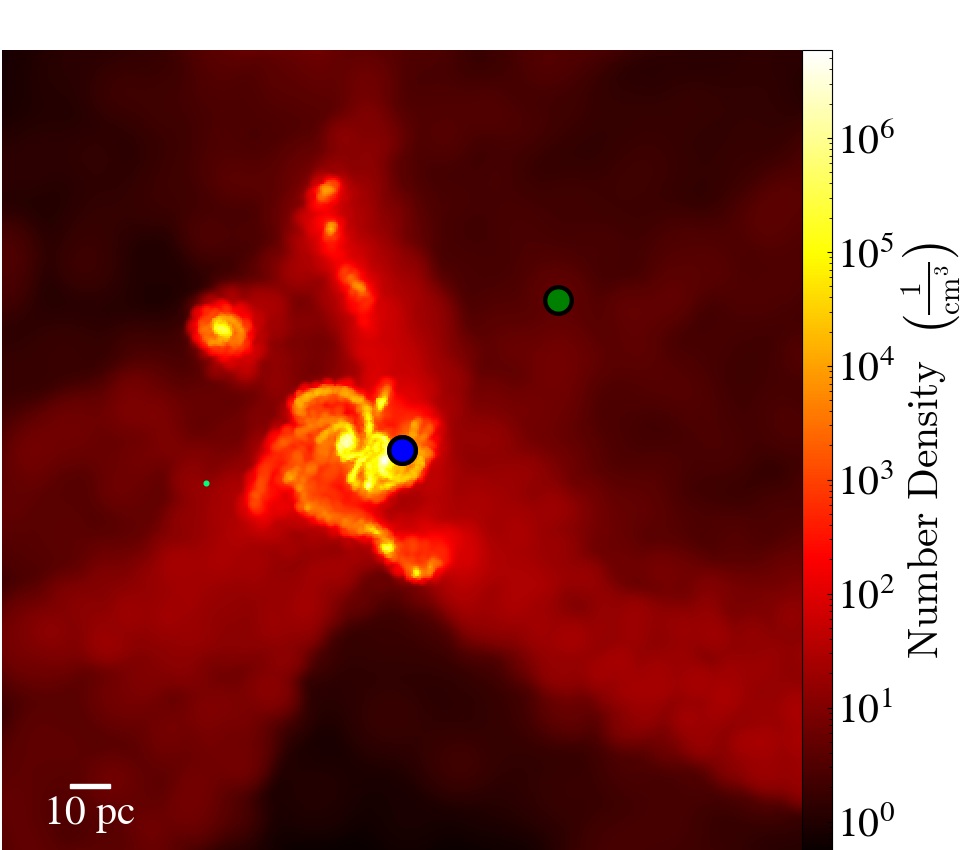
Next one up, one of four published on Thursday 10th July, is “Predicting the number density of heavy seed massive black holes due to an intense Lyman-Werner field” by Hannah O’Brennan (Maynooth University, Ireland) and 7 others based in Ireland, USA and Italy. This paper presents an exploration of the scenario for black hole formation driven by Lyman-Werner photons (i.e. ultraviolet radiation in the range 11.2 to 13.6 eV). It is in the folder marked Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics, and the overlay is here:
You can read the final accepted version on arXiv here.
The fourth paper this week, and the second published on 10th July, is “Chemical Abundances in the Metal-Poor Globular Cluster ESO 280-SC06: A Formerly Massive, Tidally Disrupted Globular Cluster” by Sam A. Usman (U. Chicago, USA) and 8 others based in the USA, Canada and Australia. This paper, which is in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, presents a detailed spectroscopic study of the chemical abundances in a Milky Way globular cluster ESO 280-SC06. The overlay is here:

The officially accepted version of the paper can be read here.
Next one up, also published on 10th July and also in the folder marked Astrophysics of Galaxies is “Predictions for the Detectability of Milky Way Satellite Galaxies and Outer-Halo Star Clusters with the Vera C. Rubin Observatory” by Kabelo Tsiane (U. Michigan) and 9 others on behalf of the LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration.
The overlay is here:

You can find the officially-accepted version of the paper on arXiv here.
The penultimate paper for this week, and the last of the batch published on 10th July, is “Systematically Measuring Ultra-Diffuse Galaxies. VIII. Misfits, Miscasts, and Miscreants” by Dennis Zaritsky, Richard Donnerstein, and Donghyeon J. Khim (Steward Observatory, U. Arizona, USA). This paper presents a morphological study of weird and wonderful galaxies as part of an effort to Systematically Measure Ultra-Diffuse Galaxies (the SMUDGes survey). It is in the folder marked Astrophysics of Galaxies. The overlay is here:
You can find the officially-accepted version of the paper on arXiv here.
The last article published this week is “Differential virial analysis: a new technique to determine the dynamical state of molecular clouds” by Mark R. Krumholz (ANU, Australia), Charles J. Lada (Harvard, USA) & Jan Forbrich (U. Herts, UK). This paper presents simple analytic models of supported and collapsing molecular clouds, tested using full 3D simulations and applied to observed clouds in Andromeda. It is in the folder marked Astrophysics of Galaxies and was published yesterday, i.e on Friday 11th July 2025. Here is the overlay

You can find the officially-accepted version on arXiv here.
And that’s all the papers for this week. I will, however, take this opportunity to mention that a while ago I was interviewed about the Open Journal of Astrophysics by Colin Stuart on behalf of the Foundational Questions Institute; the write-up of the interview can be found here.