It’s Saturday again, so it’s time for a summary of the week’s new papers at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Since the last update we have published five new papers, which brings the number in Volume 8 (2025) up to 141, and the total so far published by OJAp up to 376.
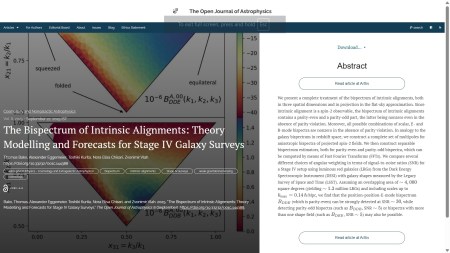
The first paper to report this week is “The Bispectrum of Intrinsic Alignments: Theory Modelling and Forecasts for Stage IV Galaxy Surveys” by Thomas Bakx (Utrecht U., NL), Alexander Eggemeier (U. Bonn, DE), Toshiki Kurita (MPA Garching, DE), Nora Elisa Chisari (Leiden U., NL) and Zvonimir Vlah (Ruđer Bošković Institute, Croatia). This paper was published on Monday 22nd September 2025 in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics. It studies the bispectrum of intrinsic galaxy alignments, a possible source of systematic errors in extracting cosmological information from the analysis of weak lensing surveys.
The overlay is here:
You can make this larger by clicking on it. The officially accepted version of this paper can be found on the arXiv here.
The second paper this week, published on Tuesday 23rd September 2025 is “Reanalysis of Stage-III cosmic shear surveys: A comprehensive study of shear diagnostic tests” by Jazmine Jefferson (University of Chicago, USA) and 13 others for the LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration. It is also in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics; it describes diagnostic tests on three public shear catalogs (KiDS-1000, Year 3 DES-Y3 s, and Year 3 HSC-Y3); not all the surveys pass all the tests.
The corresponding overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here.
The third one this week, published on Wednesday 24th September 2025 in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, is “Is feedback-free star formation possible?” by Andrea Ferrara, Daniele Manzoni, and Evangelia Ntormousi (all of the Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa, Italy). This paper presents an argument that Lyman-alpha radiation pressure strongly limits star formation efficiency, even at solar metallicities, so that a feedback-free star formation phase is not possible without feedback. The overlay is here:
You can find the officially-accepted version on arXiv here.
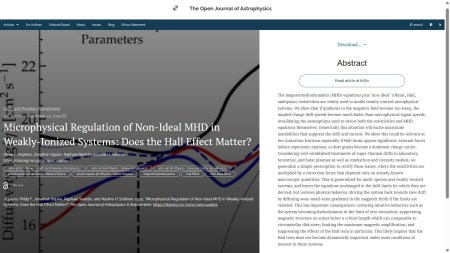
Next we have “Microphysical Regulation of Non-Ideal MHD in Weakly-Ionized Systems: Does the Hall Effect Matter?” by Philip F. Hopkins (Caltech, USA), Jonathan Squire (U. Otago, New Zeland), Raphael Skalidis (Caltech) and Nadine H. Soliman (Caltech). This was also published on Wednesday 24th September 2025, but in the folder Earth and Planetary Astrophysics. It presents an improved treatment of non-ideal effects in magnetohydrodynamics, particularly the Hall effect, and a discussion of the implications for weakly-ionized astrophysical systems.
The corresponding overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version of this one on arXiv here.
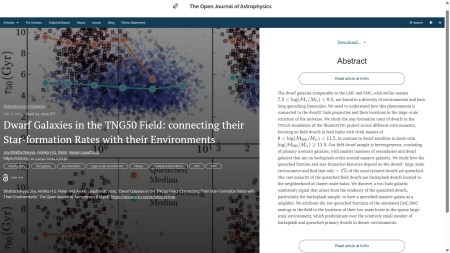
The fifth, and last, one for this week is “The Local Volume Database: a library of the observed properties of nearby dwarf galaxies and star clusters” by Andrew B. Pace (University of Virginia, USA). This one was published on Friday 26th September (i.e. yesterday) in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies. It presents a catalogue of positional, structural, kinematic, chemical, and dynamical parameters for dwarf galaxies and star clusters in the Local Volume. The overlay is here:
You can find the officially-accepted version of this paper on arxiv here.
And that concludes the report for this week. I’ll post another update next Saturday.