I was thinking last weekend that in, all the time I’ve spent in Barcelona this year, and all the times I’ve travelled through the Metro station called Liceu, I’ve never been inside the Gran Teatre del Liceu. I decided to remedy that by booking a ticket to see last night’s performance of Bluebeard’s Castle, a one-act Opera by Béla Bartók. The theatre is actually on La Rambla, and I had to dodge through the hordes of tourists to get there, but it’s an easy walk from my apartment.
El Liceu is indeed very beautiful inside and deserves its reputation as one of the world’s finest opera houses. The main hall is about the same size as that of the Royal Opera House in Covent Garden, with a seating capacity of over 2,000, and it does have a similar decor, with red and gold everywhere. When I booked my ticket (on Monday) there were plenty of seats available to choose from, so I wondered what the attendance would be like. As it turned out, it wasn’t quite full but there was a good crowd in.
I have seen Bluebeard’s Castle a couple of times before, but it surprises me that there are no old reviews in my back catalogue on this blog. From that observation I deduce that both times I saw it were before 2008, which is when I started blogging. I do think it’s a masterpiece, however, which is why I jumped at the chance to see and hear it again. Last night’s was a concert performance, i.e. without staging, which works well with this Opera as there are only two principals and it sometimes it’s good to leave a lot to the listener’s imagination. The performance was in the original Hungarian language, with surtitles provided in Catalan, Spanish and English.
The Opera is based on a French folk legend of Bluebeard, a murderous character foreshadowing Jack the Ripper, and Judith, who has for some reason fallen in love with him, despite it being widely believed that he murdered his previous wives. She travels with him to his castle and, when they arrive, she starts to ask Bluebeard some uncomfortable questions as she makes her way through the dark castle. Seven doors appear to which Bluebeard holds the keys. Each one will reveal information about the personality and past of a Bluebeard. The first door opens to reveal a blood-soaked torture chamber, for example. And that’s just the start…
The final door reveals his former wives, apparently still alive. But are they ghosts? Who knows? Judith doesn’t seem to mind. She becomes the fourth wife and disappears into the darkness enfolding the other three. That’s the end.
The Opera doesn’t really have that much to do with the folk story. It is really an allegory – the rooms contain secrets of Bluebeard’s past, including past relationships, which he has locked away deep inside himself. Only Judith’s persistent questioning can persuade him to reveal them.
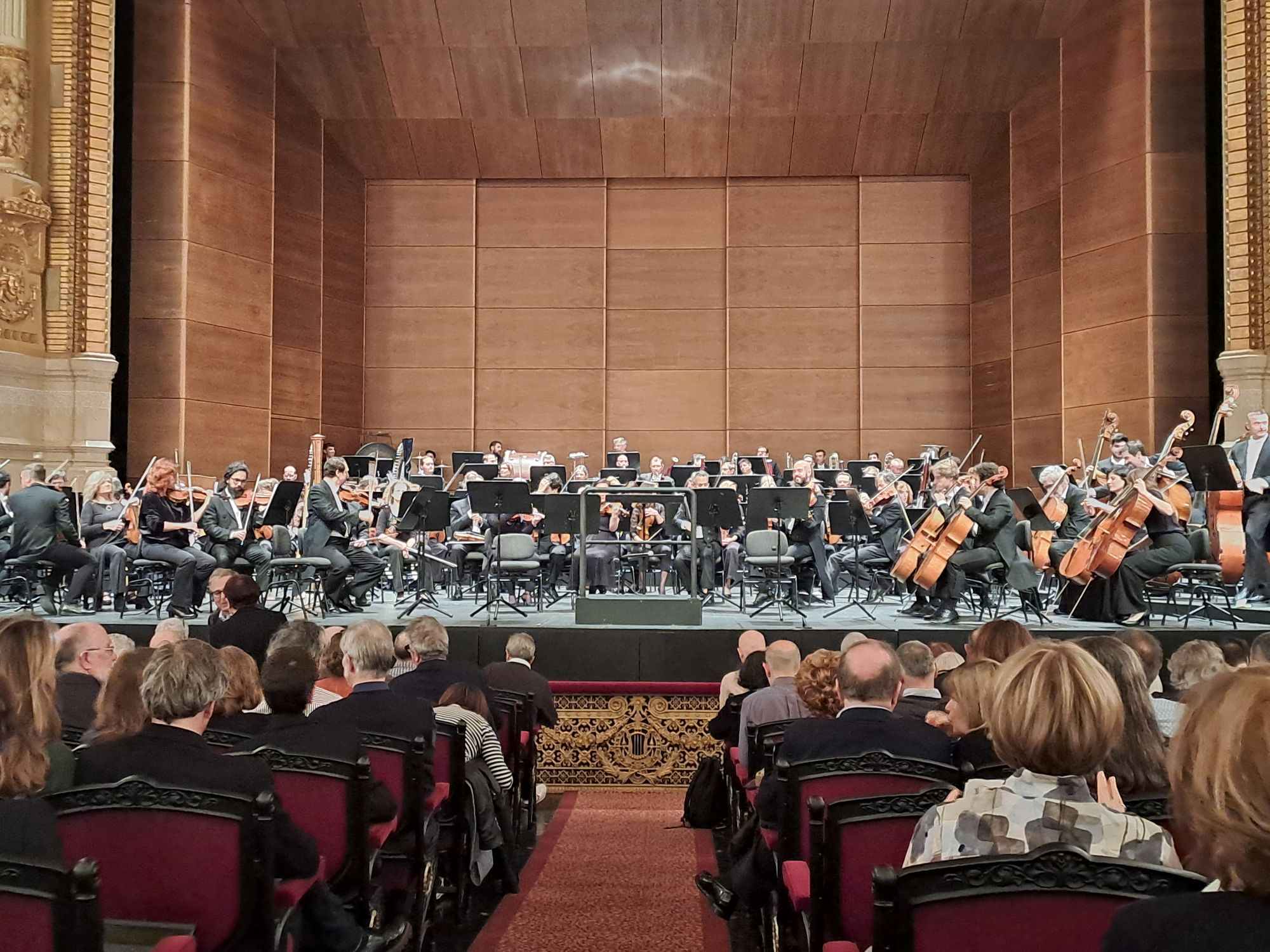
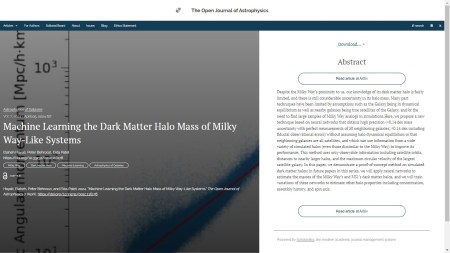
The music for Bluebeard’s Castle is extraordinarily rich and varied, changing as each door is opened. A large orchestra is needed to produce these changes of texture, as you can see in the picture I took before the performance. The musicians, under the direction of Josep Pons, played superbly as well as supplying eery sighs when the libretto demanded it. Vocals were supplied by bass-baritone Nicholas Brownlee as Bluebeard and mezzo soprano Victoria Karkacheva; both were excellent.
The performance lasted only about an hour. One of the things about going to an Opera in the evening is that one usually has to have something to eat before the performance, because it’s likely to be too late afterwards to find anywhere still serving food. That doesn’t apply here in Spain, where people generally eat rather late. I was thinking as I left last night that it was the first time I had been to an Opera that started at 7.30pm after which it was still too early to have dinner!