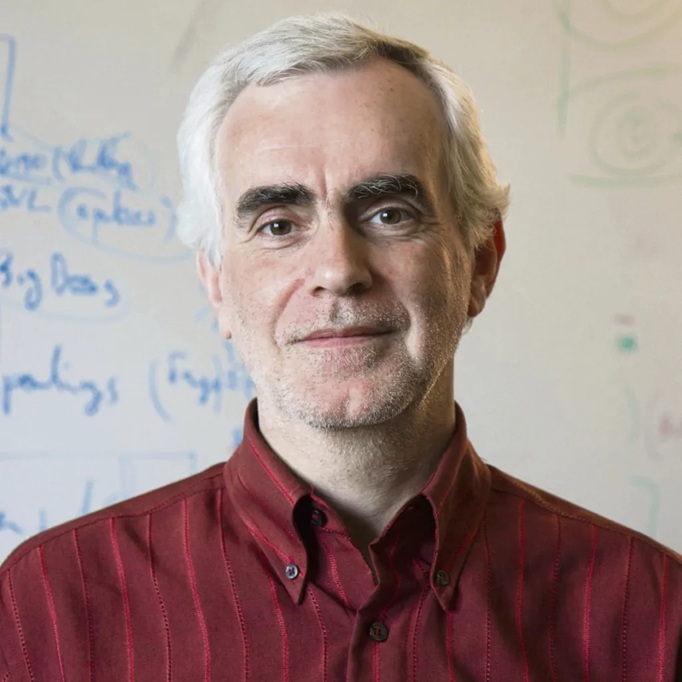
Last night I received a message via the Euclid Consortium conveying the very sad news of the death, at the age of 67, of the French astrophysicist and cosmologist Yannick Mellier (pictured left). Among many other things, Yannick was the Euclid Consortium Lead in which role he took on enormous responsibility for getting the project started and, with his team, keeping everything running. His loss is incalculable.
Yannick’s research work focussed on cosmology and the search for dark matter using gravitational lensing. Back in 1987 he was part of the observational team that discovered the first giant arc produced by strong gravitational lensing. He also did pioneering work in the field of weaking gravitational lensing with the Canada-France Hawaii Telescope in that regard starting back in 2000.
For well over a decade now Yannick had been involved with the European Space Agency’s Euclid mission. He was a major force right from the beginning, making the proposal, and after it was accepted leading the Consortium assembled to bring the project into being, preparing for launch, and dealing with the first data. The Euclid Consortium is a huge collaboration and it is impossible to overestimate the scale of the task facing the Lead. The first full data release (DR1) from Euclid will take place towards the end of next year (2026). It is sad beyong words that he did not live to see this.
During the period when I was Chair of the Euclid Consortium Diversity Committee I had a number of interactions with Yannick, sometimes dealing with difficult and confidential matters. I found him to be a man of great wisdom and sensitivity. Despite having many other things to deal with, including a long-term illness, he was unfailingly supportive and his advice was always sound.
The following is an excerpt from the message sent out yesterday:
Yannick’s death leaves a huge void within the consortium and our community. Those of us who have been here the longest know how hard he worked to make the Euclid project a success. He became its embodiment, working tirelessly to ensure its success; we owe him an immense debt of gratitude, and we will surely have the opportunity to reflect in detail on all that we owe him.
Indeed. I hope the Euclid Consortium – and the international cosmological community generally – will, at some stage, organize an appropriate tribute to Yannick.
Rest in Peace, Yannick Mellier (1958-2025)
Ar dheis Dé go raibh a anam