Time for the weekly Saturday morning update of papers published at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Since the last update we have published four new papers, which brings the number in Volume 8 (2025) up to 25 and the total so far published by OJAp up to 260.
In chronological order of publication, the four papers published this week, with their overlays, are as follows. You can click on the images of the overlays to make them larger should you wish to do so.
The first paper to report is “Partition function approach to non-Gaussian likelihoods: information theory and state variables for Bayesian inference” by Rebecca Maria Kuntz, Heinrich von Campe, Tobias Röspel, Maximilian Philipp Herzog, and Björn Malte Schäfer, all from the University of Heidelberg (Germany). It was published on Wednesday March 5th 2025 in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics and it discusses the relationship between information theory and thermodynamics with applications to Bayesian inference in the context of cosmological data sets.
You can read the officially accepted version of this paper on arXiv here.
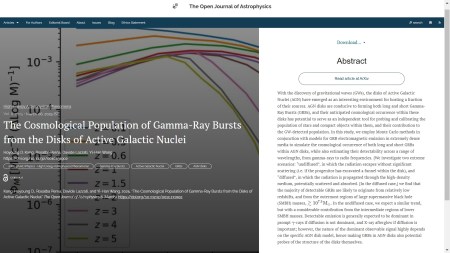
The second paper of the week is “The Cosmological Population of Gamma-Ray Bursts from the Disks of Active Galactic Nuclei” by Hoyoung D. Kang & Rosalba Perna (Stony Brook), Davide Lazzati (Oregon State), and Yi-Han Wang (U. Nevada), all based in the USA. It was published on Thursday 6th March 2025 in the folder High-Energy Astrophysical Phenomena. The authors use models for GRB electromagnetic emission to simulate the cosmological occurrence and observational detectability of both long and short GRBs within AGN disks
You can find the officially accepted version of this paper on arXiv here.
The next two papers were published on Friday 7th March 2025.
“The distribution of misalignment angles in multipolar planetary nebulae” by Ido Avitan and Noam Soker (Technion, Haifa, Israel) analyzes the statistics of measured misalignment angles in multipolar planetary nebulae implies a random three-dimensional angle distribution limited to <60 degrees. It is in the folder Solar and Stellar Astrophysics.
Here is the overlay:
The official published version can be found on the arXiv here.
The last paper to report this week is “The DESI-Lensing Mock Challenge: large-scale cosmological analysis of 3×2-pt statistics” by Chris Blake (Swinburne, Australia) and 43 others; this is a large international collaboration and I apologize for not being able to list all the authors here!
This one is in the folder marked Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics; it presents an end-to-end simulation study designed to test the analysis pipeline for the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Year 1 galaxy redshift dataset combined with weak gravitational lensing from other surveys.
The overlay is here:
You can find the “final” version on arXiv here.
That’s all for this week. It’s good to see such an interesting variety of topics. I’ll do another update next Saturday