It’s Saturday once more so time for another update of activity at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Since the last update we have published a further six papers, bringing the number in Volume 9 (2026) to 36 and the total so far published by OJAp up to 484.
I will continue to include the posts made on our Mastodon account (on Fediscience) to encourage you to visit it. Mastodon is a really excellent service, and a more than adequate replacement for X/Twitter (which nobody should be using); these announcements also show the DOI for each paper.
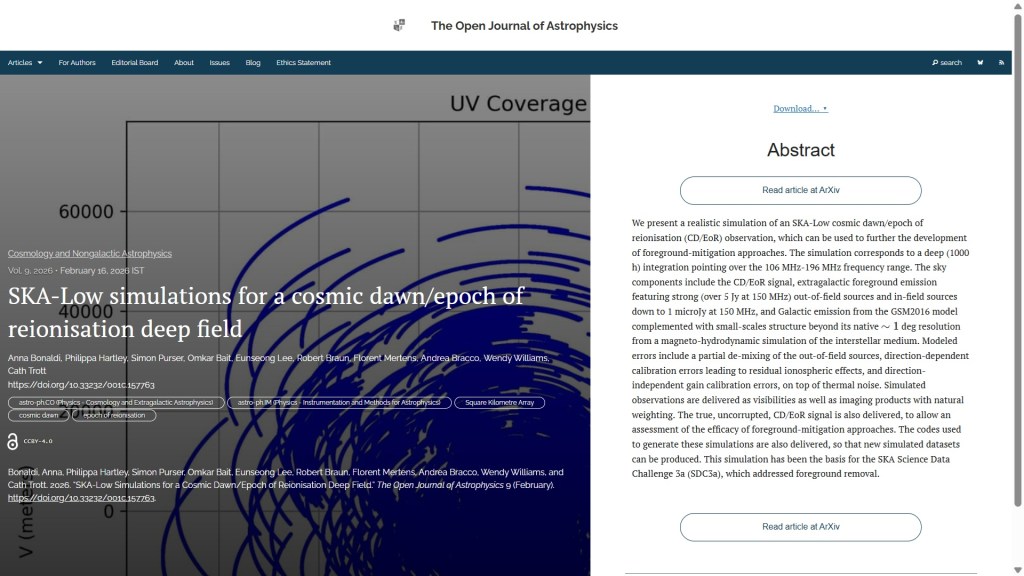
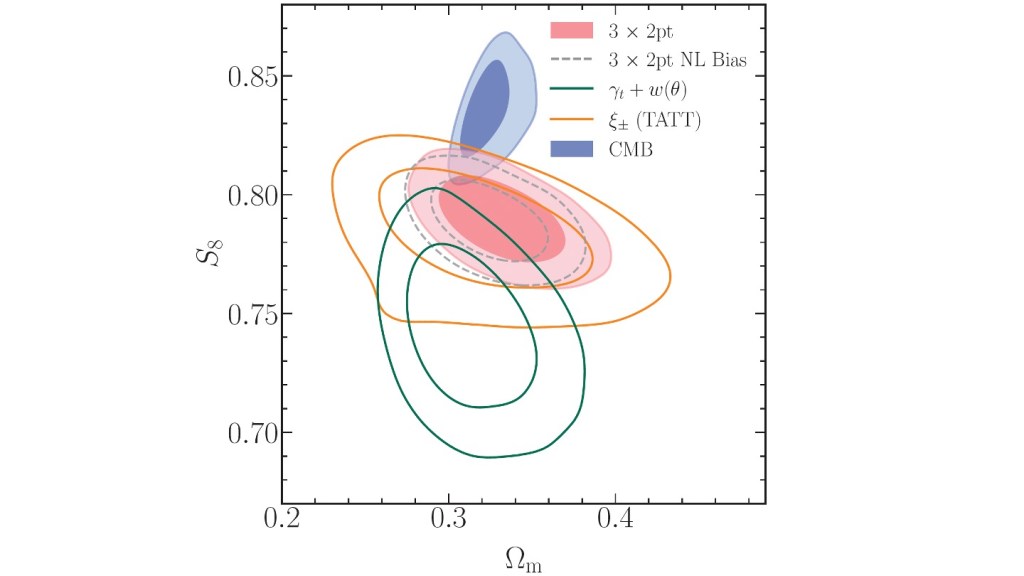
The first paper to report this week is “SKA-Low simulations for a cosmic dawn/epoch of reionisation deep field” by Anna Bonaldi, Philippa Hartley, Simon Purser & Omkar Bait (SKAO, UK), Eunseong Lee (U. Manchester, UK), Robert Braun (SKAO), Florent Mertens (Sorbonne Université, France), Andrea Bracco (Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, IT), Wendy Williams (SKAO) and Cath Trott (Curtin U., Australia). This paper presents a simulation of an SKA-Low cosmic dawn/epoch of reionisation observation to advance foreground-mitigation approaches: the simulation includes various sky components and modelled errors, allowing for efficacy assessment. It was published on Monday 16th February in the folder Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics.
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the announcement on Fediverse here:
The second paper is “V717 Andromedae: An Active Low Mass Ratio Contact Binary” by Surjit S. Wadhwa (Western Sydney U. Australia), Marko Grozdanovic (Astronomical Observatory Belgrade, Serbia), and Nicholas F.H Tothill, Miroslav D. Filipovic, Ain Y. De Horta (Western Sydney U.). This was also published on Monday 1th February, but in the folder Solar and Stellar Astrophysics. The article discusses the contact binary V717 Andromedae, an extreme low mass ratio system with high inclination and moderate contact, showing signs of chromospheric activity but stable and not a merger candidate
The overlay for this one is here:
The official version of the paper can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement here:
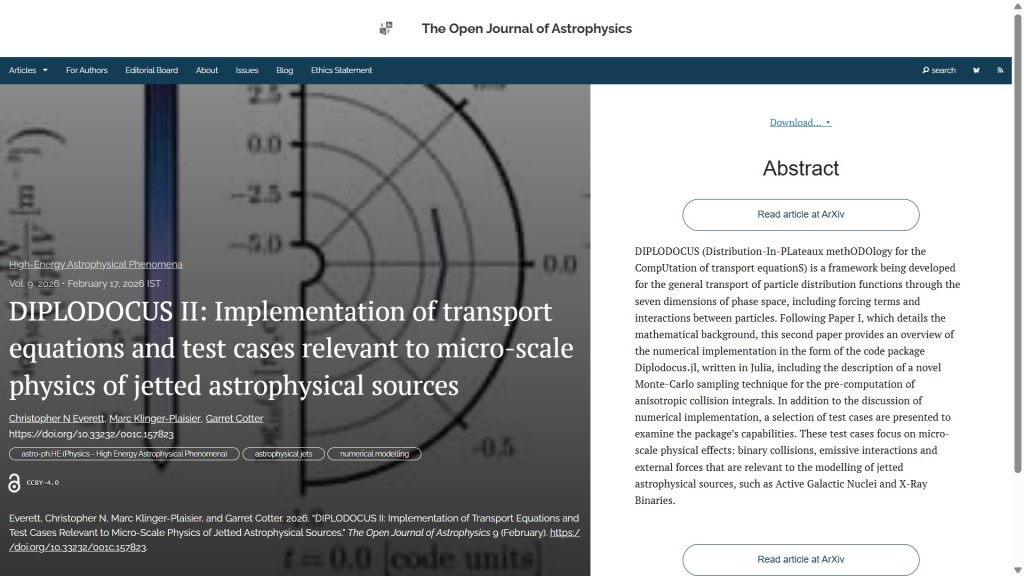
Next, published on Tuesday 17th February in the folder High-Energy Astrophysical Phenomena, is “DIPLODOCUS II: Implementation of transport equations and test cases relevant to micro-scale physics of jetted astrophysical sources” by Christopher N Everett (Oxford U., UK), Marc Klinger-Plaisier (U. Amsterdam, NL) and Garret Cotter (Oxford). This one discusses further applications of DIPLODOCUS, which is a framework developed for particle distribution transport, with its numerical implementation detailed in Diplodocus.jl. It uses a new sampling technique and is tested on micro-scale physical effects. The first paper in the series can be found here.
The overlay is here:
The official version can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement is here:
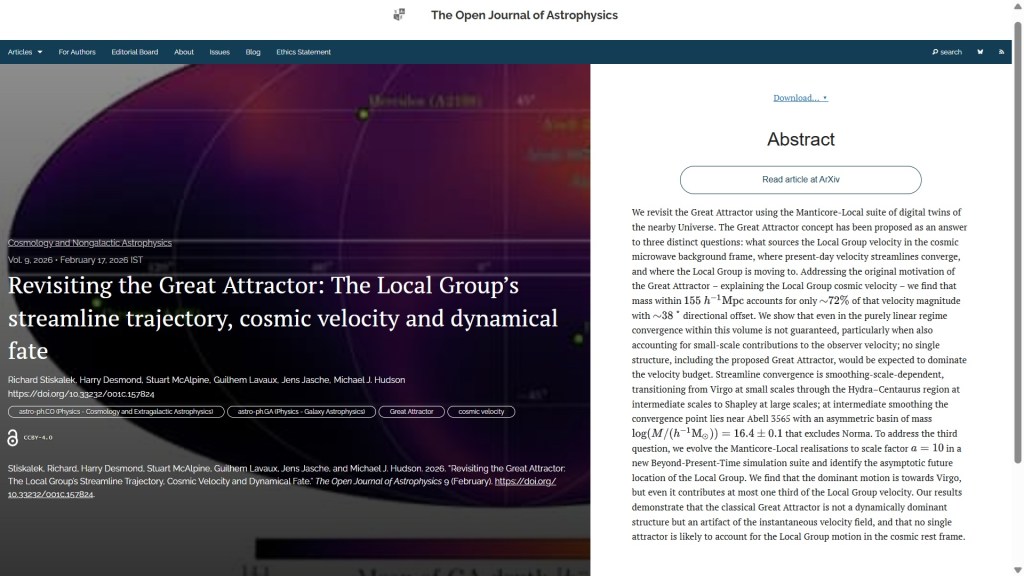
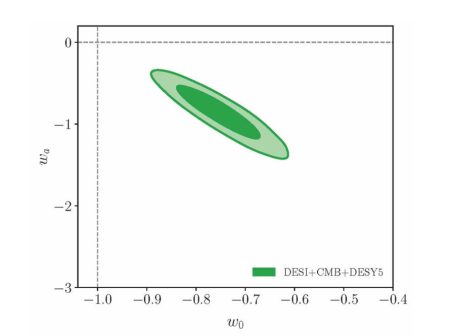
The fourth paper this week, also published on Tuesday 17th February, but in the folder Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics is “Revisiting the Great Attractor: The Local Group’s streamline trajectory, cosmic velocity and dynamical fate” by Richard Stiskalek (Oxford U., UK), Harry Desmond (U. Portsmouth, UK), Stuart McAlpine (Stockholm, SE), Guilhem Lavaux (Sorbonne Université, FR), Jens Jasche (Stockholm) and Michael J. Hudson (U. Waterloo, Canada). This paper revisits the so-called “Great Attractor” concept, finding that it doesn’t dominate the Local Group’s cosmic velocity; multiple structures contribute to the motion, with no single attractor accounting for the flow.
Here is the overlay:
The official version can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement is here:
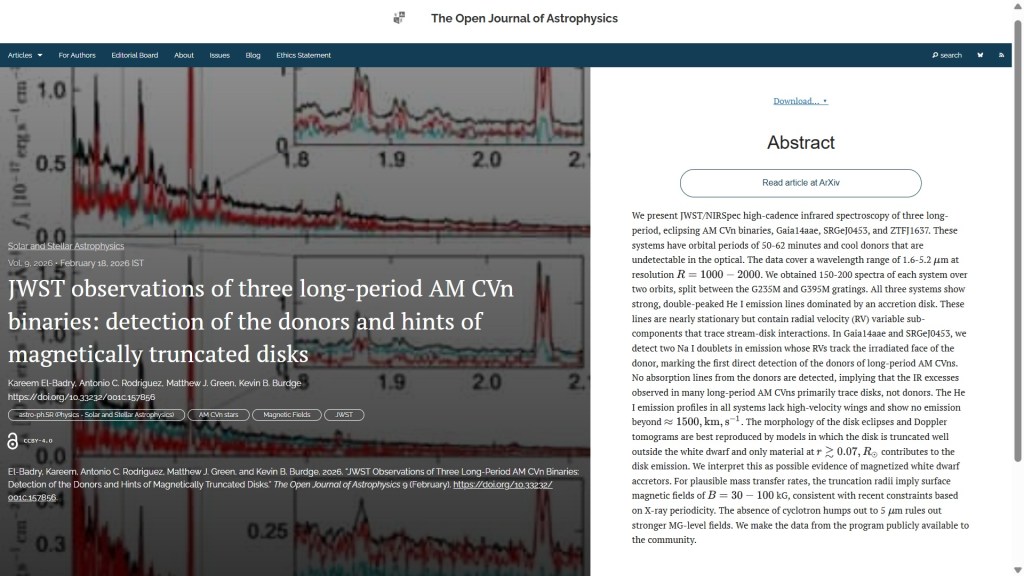
The fifth paper this week, is “JWST observations of three long-period AM CVn binaries: detection of the donors and hints of magnetically truncated disks” by Kareem El-Badry (Caltech), Antonio C. Rodriguez (CfA Harvard), Matthew J. Green (U. Oklahoma) & Kevin B. Burdge (MIT); all based in the USA. The article was published on Thursday 19th February 2026 in the folder Solar and Stellar Astrophysics. The paper describes high-cadence infrared spectroscopy used to analyze three long-period, eclipsing AM CVn (AM Canum Venaticorum) binaries; findings suggest the presence of magnetized white dwarf accretors, with surface magnetic fields of 30-100 kG.
The overlay is here:
The accepted version can be found on arXiv here, and the fediverse announcement is here:
Finally for this week we have “Ultra-long Gamma-ray Bursts from Micro-Tidal Disruption Events: The Case of GRB 250702B” by Paz Beniamini (Open University, IL), Hagai B. Perets (Technion, IL) and Jonathan Granot (Open University, IL); all based in Israel. The paper was published on Friday 18th February 2026 in the folder High-Energy Astrophysical Phenomena.
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the Mastodon announcement is here:
And that concludes this week’s update. I will do another next Saturday, by which time I expect we will have published a similar number of papers to this week.