It’s Saturday once more, so it’s time for another update of activity at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. It has been a busy week. Since the last update we have published a further nine papers, bringing the number in Volume 9 (2026) to 45 and the total so far published by OJAp up to 493.
I will continue to include the posts made on our Mastodon account (on Fediscience) to encourage you to visit it. Mastodon is a really excellent service, and a more than adequate replacement for X/Twitter (which nobody should be using); these announcements also show the DOI for each paper.
The first four papers this week were all published on Monday 23rd February.
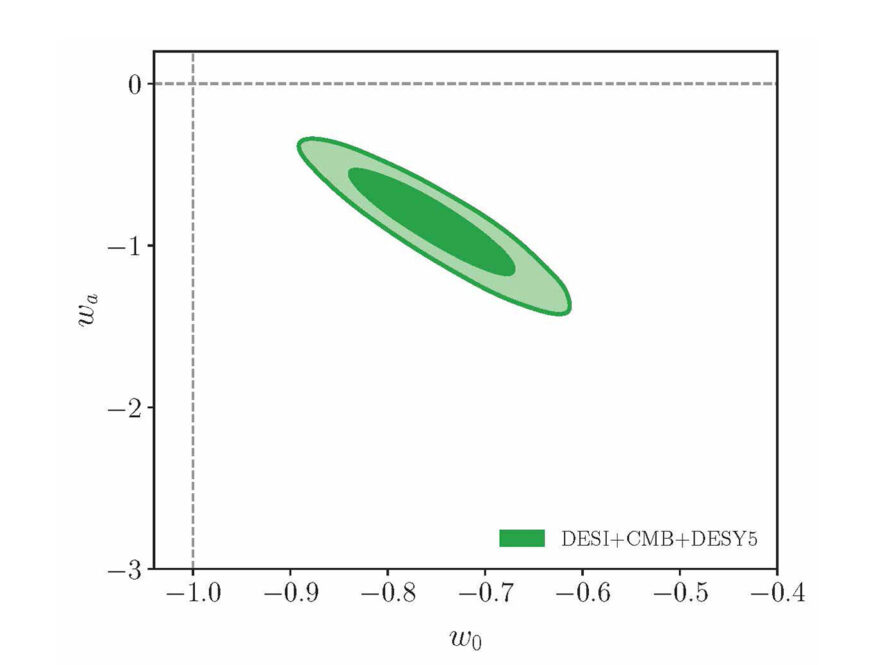
The first paper to report is “A Bayesian Exploration of The Mass of the Ursa Major III: Kinematics, Rotation and their influence on the Mass to Light Ratio” by Tim R. Adams (U. Sydney, Australia), Brendon J. Brewer (U. Auckland, New Zealand) and Geraint F. Lewis (Sydney). This paper, in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, describes an investigation of the kinematics of potential ultra-faint dwarf galaxy UMa III/U1, finding a preference for a non-rotating model; the object’s nature remains uncertain.
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the announcement on Fediverse here:
The second paper is “The Impact of Baryonic Effects on the Dynamical Masses Inferred Using Satellite Kinematics” by Josephine F.W. Baggen, Frank C. van den Bosch, and Kaustav Mitra (Yale U., USA). This paper, also in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, presents a model to assess the impact of stars and gas on satellite kinematics, showing that these baryonic effects can reduce the satellite velocity dispersion and increase inferred central galaxy masses.
The overlay for this one is here:
The official version of the paper can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement here:
The third paper this week, and the third published on Monday 23rd February, and the third in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, is “MEGATRON: Disentangling Physical Processes and Observational Bias in the Multi-Phase ISM of High-Redshift Galaxies” by Nicholas Choustikov (U. Oxford, UK) and 12 others based in UK, USA, France, Korea and Belgium. The study uses MEGATRON simulations to analyze the interstellar medium (ISM) of high-redshift galaxies, finding it denser and less metal-enriched than local galaxies with implications for line ratios as diagnostics
The overlay is here:
The official version can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement is here:
The fourth paper this week, also published on Monday 23rd February, but in the folder Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics, is “Redshift Assessment Infrastructure Layers (RAIL): Rubin-era photometric redshift stress-testing and at-scale production” by the RAIL Team (31 authors) and the Dark Energy Science Collaboration. The article introduces Redshift Assessment Infrastructure Layers (RAIL), an open-source Python library for large-scale probabilistic photo-z estimation, useful for extragalactic research and not limited to LSST data.
Here is the overlay:
The official version can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement is here:
Moving on to Tuesday 24th February, the fifth paper this week, is “Feedback shaped the galaxy morphological sequence in presence of mergers” by Masafumi Noguchi (Tohoku University, Japan). This article was published in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies. This study suggests that galaxy morphology, specifically the mass ratios of bulges and disks, is influenced by galaxy mergers and feedback processes from active galactic nuclei and supernovae.
The overlay is here:
The accepted version can be found on arXiv here, and the fediverse announcement is here:
The sixth paper this week is “HelioSpectrotron 5000: an interactive solar atlas” by Alexander G.M. Pietrow (AIP Potsdam, Germany). This was published on Tuesday 24th February in the folder Solar and Stellar Astrophysics. This describes HelioSpectrotron~5000 (HS5000), which is an interactive solar spectral atlas that allows comparison between high-resolution spectra and ground-based instrument observations, aiding in wavelength calibration and line identification. The software can be found here; I had a play with it yesterday and it’s very easy to use!
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the Mastodon announcement is here:
The seventh paper of this week was published on Thursday 26th February is “The Rise of Ionized Gas Filaments in Early-Type Galaxies” by Ryan Eskenasy (U. Kentucky, USA), Valeria Olivares (Universidad de Santiago de Chile) and Yuanyuan Su (U. Kentucky, USA). This article, in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies, is an exploration of the formation of multiphase filamentary nebulae in early-type galaxies (ETGs), using VLT-MUSE IFU observations of 126 non-central ETGs, focussing on the hot gas components thereof.
The overlay is here:
The officially accepted version of this paper can be found on the arXiv here and the Mastodon announcement is here:
Number eight for this week is “Relationship Between Major Stellar Physical Parameters and Normal Mode Frequencies in Accreting White Dwarf Stars” by Praphull Kumar, Dean M. Townsley and Hunter Anz (U. Alabama, USA). This was published on Thursday 26th February in the category Solar and Stellar Astrophysics; the paper presents a new method for identifying pulsation modes in white dwarfs, improving upon previous models by using more realistic parameters and considering thermohaline mixing and element diffusion. The overlay is here:
The final version of this paper can be found on the arXiv here and the Mastodon announcement is here:
The ninth, and final, paper for this week is “A Semi-Supervised Learning Method for the Identification of Bad Exposures in Large Imaging Surveys” by Yufeng Luo (U. Wyoming, USA) and 8 others from the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys Team. This was published on Friday 27th February, i.e yesterday, in the folder Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics. The paper describes a machine-learning approach for detecting poor-quality exposures in large astronomical imaging surveys, proving efficient and accurate in identifying problematic exposures.
The overlay is here:
The official version on arXiv can be found here and the Mastodon announcement follows:
And that concludes this week’s update. We have now published 45 papers in two complete months of 2026, on which basis we can estimate about 270 papers in the year. For the record, in the first two months of 2025 we published 21 papers.
P.S. Thank you to the many people who responded to the latest call for editors. I’ve been sending out invitations and getting people onboard as quickly as I can, but I still have a number to get to so please bear with me!