It may be a Bank Holiday weekend here in Ireland, but it’s still time for the usual Saturday update of the week’s new papers at the Open Journal of Astrophysics (although a bit later in the day than usual). Since the last update we have published another five papers, which brings the number in Volume 8 (2025) up to 161, and the total so far published by OJAp up to 396.
This week’s update is rather unusual because there are four papers in a series (or, more precisely, mathematically speaking, a sequence) all published on the same day (Wednesday October 22nd 2025), in the same folder (Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics), with the same first author (Dhayaa Anbajagane of the University of Chicago), with long author lists and many co-authors in common. These papers all relate to the DECADE cosmic shear project. Instead of doing them one by one, therefore, I’ve decided to put all four overlays together and provide links to all the papers afterwards. As I’m trying to encourage people to follow our feed on the Fediverse via Mastodon (where I announce papers as they are published, including the all-important DOI), I’ll include links to each announcement there too.
- “The DECADE cosmic shear project I: A new weak lensing shape catalog of 107 million galaxies“, accepted version on arXiv here.
- “The DECADE cosmic shear project II: photometric redshift calibration of the source galaxy sample“, accepted version on arXiv here.
- “The DECADE cosmic shear project III: validation of analysis pipeline using spatially inhomogeneous data“, accepted version on arXiv here.
- “The DECADE cosmic shear project IV: cosmological constraints from 107 million galaxies across 5,400 deg2 of the sky“, accepted version on arXiv here.
The fediverse announcements follow:
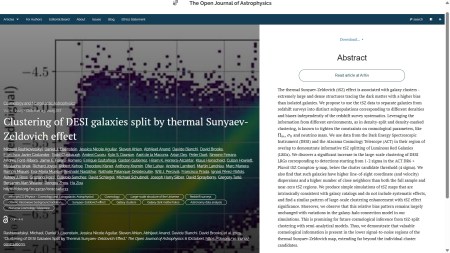
The fifth and final paper for this week is “Clustering of DESI galaxies split by thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect” by Michael Rashkovetskyi of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, or CfA for short, and 48 others. This one was published on Wednesday 23rd October in the folder Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics. This paper explores how the clustering properties of galaxies mapped by the Dark energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) relate to the local thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich emission mapped by the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT). The overlay is here:
The officially accepted version can be found on arXiv here, and the fediverse announcement is here:
That concludes the papers for this week. With one week to go and our total at 396, I still think we might reach the 400 total by the end of October.