It’s Saturday again, so it’s time for the usual update of the week’s new papers at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Publishing this week was interrupted by the Thanksgiving holiday in the United States, which meant there were no arXiv announcements yesterday. Nevertheless, since the last update we have published another four papers, which brings the number in Volume 8 (2025) up to 184, and the total so far published by OJAp up to 419.
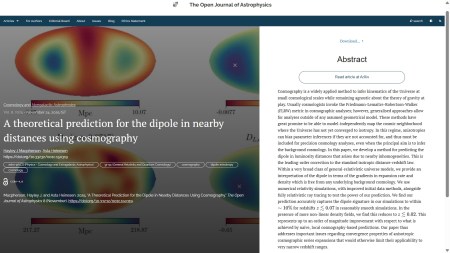
The first paper this week is “A theoretical prediction for the dipole in nearby distances using cosmography” by Hayley J. Macpherson (U. Chicago, USA) and Asta Heinesen (Niels Bohr Institute, Denmark). This was published on Monday 24th November 2025 in the folder Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics. It presents a method to predict the dipole in luminosity distances that arises due to nearby inhomogeneities to leading-order correction to the standard isotropic distance-redshift law. Incidentally, I wrote about a talk by one of the authors here.
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement is here:
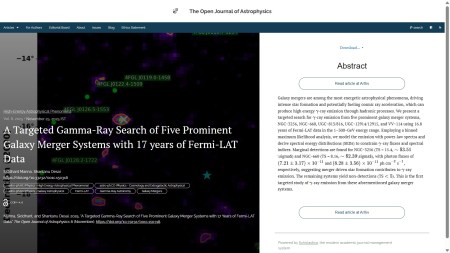
The second paper of the week is “A Targeted Gamma-Ray Search of Five Prominent Galaxy Merger Systems with 17 years of Fermi-LAT Data” by Siddhant Manna and Shantanu Desai (IIT Hyderabad Kandi, India). This one was published on Tuesday November 25th 2025 in the folder marked High-Energy Astrophysical Phenomena. It describes a search for gamma-ray emission in Fermi-LAT data from five merging galaxy systems with marginal detections for two of them
The overlay is here:
You can find the official version of this one on arXiv here. The federated announcement on Mastodon is here:
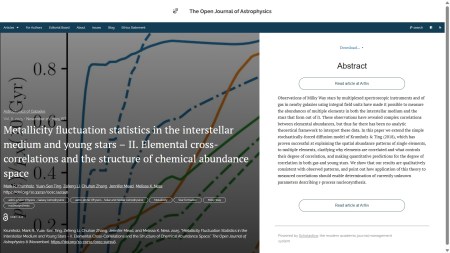
Next one up is “Metallicity fluctuation statistics in the interstellar medium and young stars – II. Elemental cross-correlations and the structure of chemical abundance space” by Mark R. Krumholz (ANU, Australia), Yuan-Sen Ting (Ohio State U., USA), Zefeng Li (Durham U., UK), Chuhan Zhang (ANU), Jennifer Mead (Columbia U., USA) and Melissa K. Ness (ANU). This was published in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies on Wednesday November 26th. It presents an extended stochastically-forced diffusion model for the chemical evolution of galaxies, making quantitative predictions for the degree of correlation in abundance patterns in both gas and young stars.
The overlay is here:
You can find the official accepted version on arXiv here. The fediverse announcement is here:
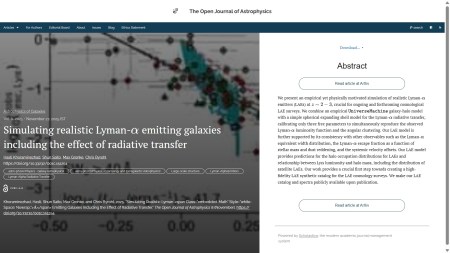
The fourth and final paper of the week is “Simulating realistic Lyman-alpha emitting galaxies including the effect of radiative transfer” by Hasti Khoraminezhad & Shun Saito (Missouri Institute of Science & Technology, USA), Max Gronke (U. Heidelberg, Germany) and Chris Byrohl (MPA Garching, Germany). An empirical model for Lyman-alpha emitters (LAEs) which provides predictions for the halo occupation distributions and relationship between luminosity and halo mass, including the distribution of satellite LAEs. It was published on Thursday November 27th 2025 in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies.
The overlay is here:
You can find the official published version on arXiv here. The Fediverse announcement follows:
And that concludes the update for this week. I will do another next Saturday.