It’s Saturday once more so time for another update of activity at the Open Journal of Astrophysics. Since the last update we have published seven papers, bringing the number in Volume 9 (2026) to 11 and the total so far published by OJAp up to 459. This week has been quite busy; for only the second time in recorded history we published at least one paper each working day.
I will continue to include the announcements made on our Mastodon account (on Fediscience) to encourage you to visit it. Mastodon is a really excellent service, and a more than adequate replacement for X/Twitter which nobody should be using.
The first three papers this week were all published on Monday January 12th in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies.
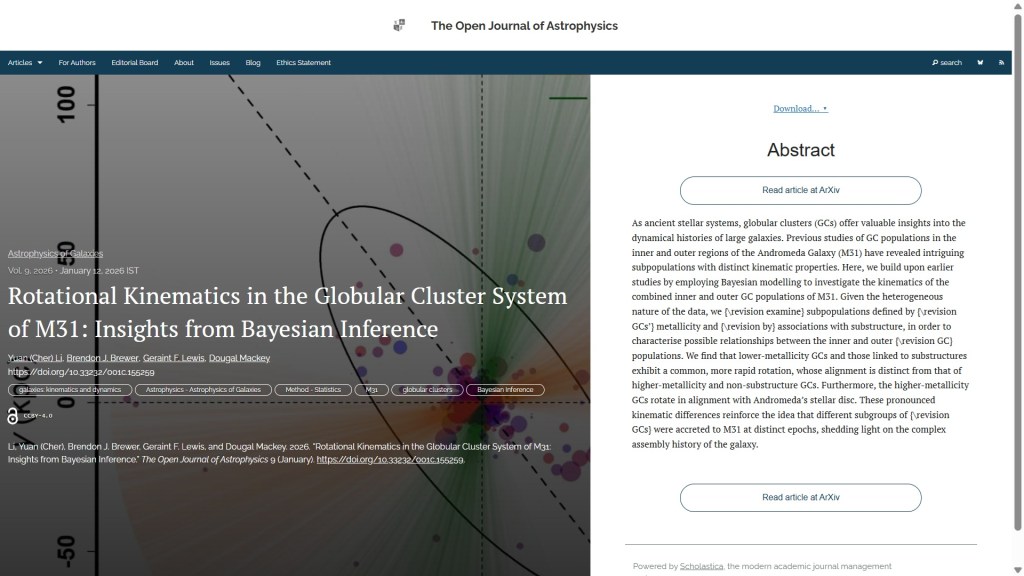
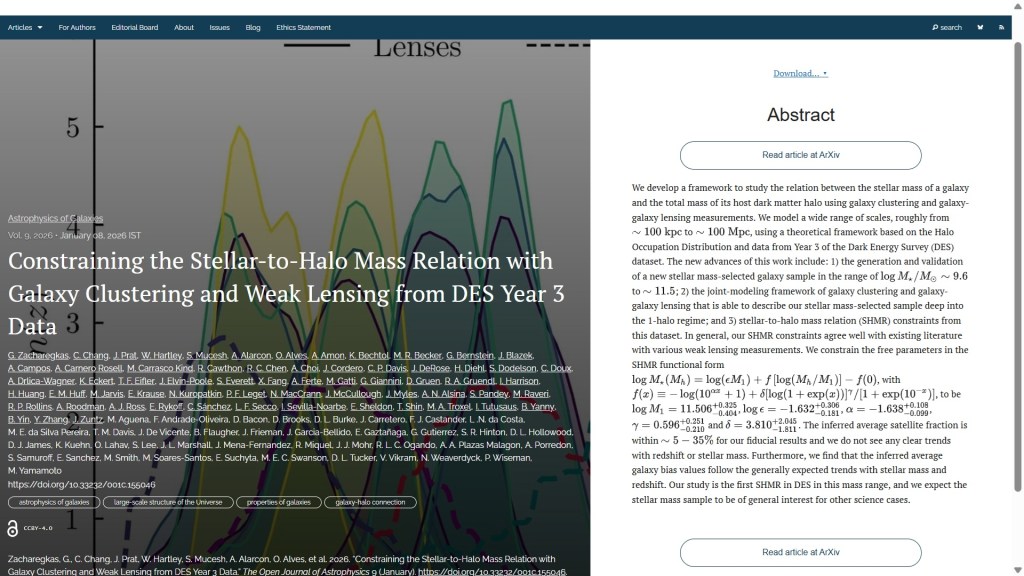
The first paper to report this week is “Rotational Kinematics in the Globular Cluster System of M31: Insights from Bayesian Inference” by Yuan (Cher) Li & Brendon J. Brewer (U. Auckland, New Zealand), Geraint F. Lewis (U. Sydney, Australia) and Dougal Mackey (independent researcher, Australia). This study uses Bayesian modelling to explore the kinematics of globular clusters in the Andromeda Galaxy, revealing distinct rotation patterns that suggest different subgroups were added at separate times.
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the announcement on Fediverse here:
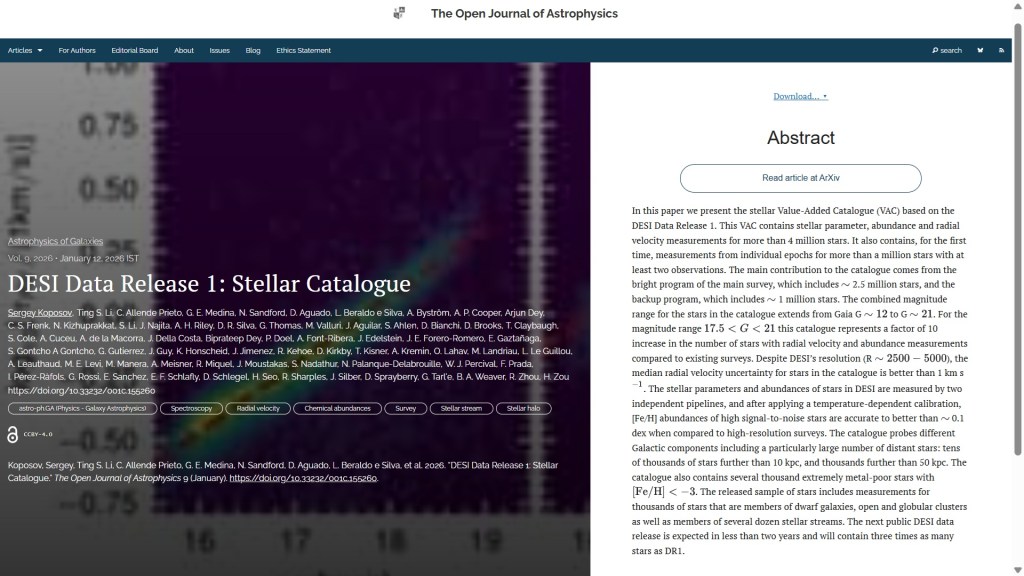
The second paper is “DESI Data Release 1: Stellar Catalogue” by Sergey Koposov (U. Edinburgh, UK) and an international cast of 67 other authors. This paper introduces and describes the stellar Value-Added Catalogue (VAC) based on DESI Data Release 1, providing measurements for over 4 million stars, including radial velocity, abundance, and stellar parameters.
The overlay for this one is here:
The official version of the paper can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement here:
Next we have “On the origins of oxygen: ALMA and JWST characterise the multi-phase, metal-enriched, star-bursting medium within a ‘normal’ z>11 galaxy” by Joris Witstok (Cosmic Dawn Centre, Copenhagen, Denmark) and 37 others in locations dotted around the world. This paper presents new ALMA observations of the JADES-GS-z11-0 galaxy confirm the presence of the [O III] 88 µm line, suggesting it consists of two low-mass components undergoing star formation and enriched in metals.
The overlay is here:
The official version can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement is here:
The fourth paper this week is also in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies. but was published on Tuesday 13th January. It is entitled “Accelerated calibration of semi-analytic galaxy formation models” by Andrew Robertson and Andrew Benson (Carnegie Observatories, USA). This paper presents a faster calibration framework for galaxy formation models, using fewer simulations for each evaluation. However, the model shows discrepancies suggesting the model needs to be made more flexible.
The overlay is here:

You can find the officially accepted version on arXiv here and the Mastodon announcement here:
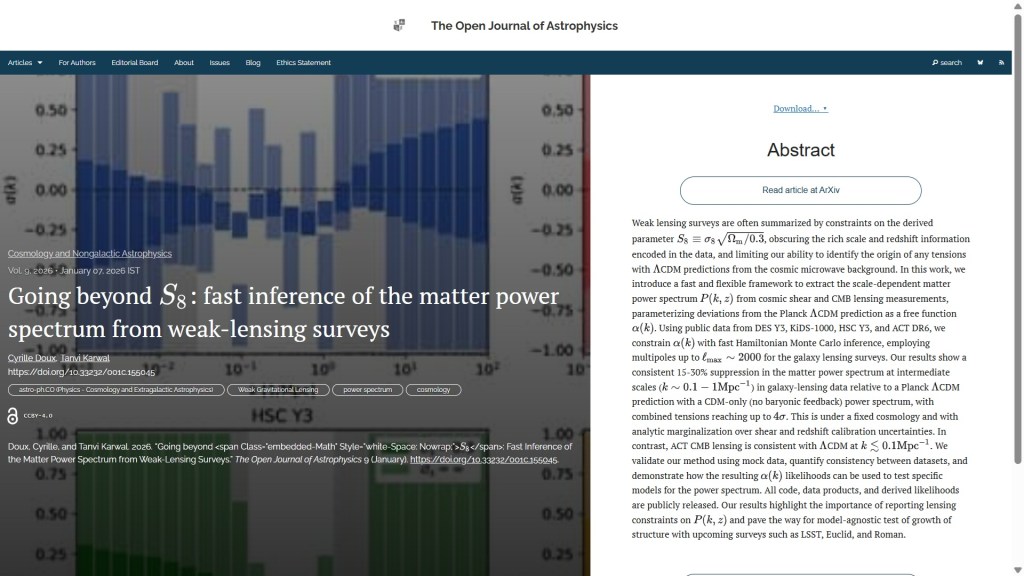
Next one up, published on Wednesday 14th January in the folder Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics, is “Constraints from CMB lensing tomography with projected bispectra” by Lea Harscouet & David Alonso (U. Oxford), UK), Andrina Nicola (U. Manchester, UK) and Anže Slosar (Brookhaven National Laboratory, USA). This study presents angular power spectra and bispectra of DESI luminous red galaxies, finding that the galaxy bispectrum can constrain the amplitude of matter fluctuations and the non-relativistic matter fraction. The overlay is here:
You can find the officially accepted paper on arXiv here and the Mastodon announcement here:
The sixth paper this week is “Universal numerical convergence criteria for subhalo tidal evolution” by Barry T. Chiang & Frank C. van den Bosch (Yale U., USA) and Hsi-Yu Schive (National Taiwan University, Taiwan). This was published on Thursday 15th January in the folder Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics; it presents an analysis of a simulation suite that addresses the ‘overmerging’ problem in cosmological simulations of dark matter subhalos, showing that up to 50% of halos in state-of-the art simulations are unresolved. The overlay is here:
The final accepted version of this paper can be found on arXiv here. The Mastodon announcement follows:
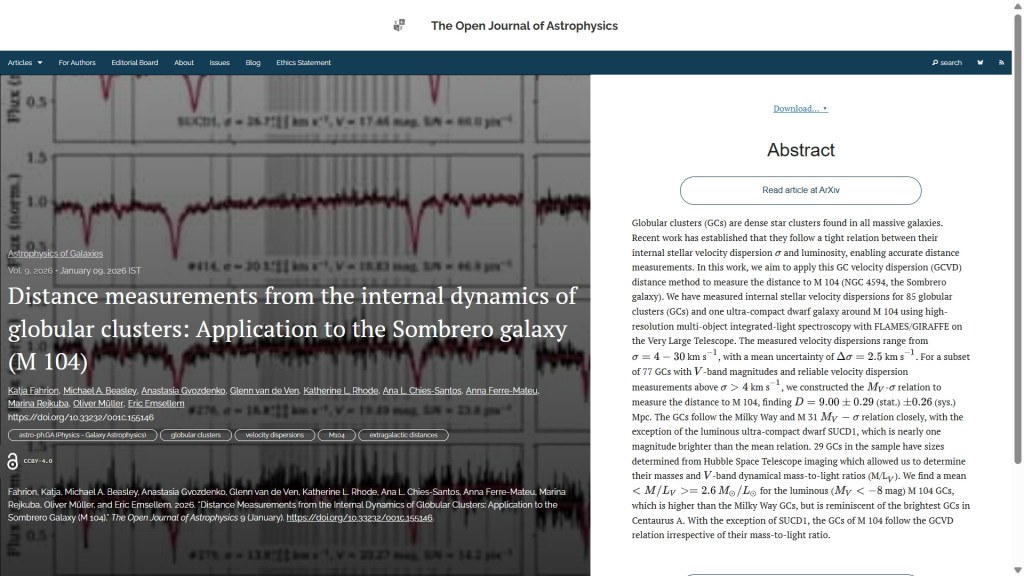
Finally for this week we have “Detectability of dark matter subhalo impacts in Milky Way stellar streams” by Junyang Lu , Tongyan Lin & Mukul Sholapurkar (UCSD, USA) and Ana Bonaca (Carnegie Observatories, USA). This was published on Friday 16th January (i.e. yesterday) in the folder Astrophysics of Galaxies. The study develops a method to estimate the minimum detectable dark matter subhalo mass in stellar streams, ranking them by sensitivity and identifying promising lines for further research.
The overlay is here:
The officially accepted version can be found on arXiv here and the Fediverse announcement here:
That concludes the update for this week. I will do another next Saturday.